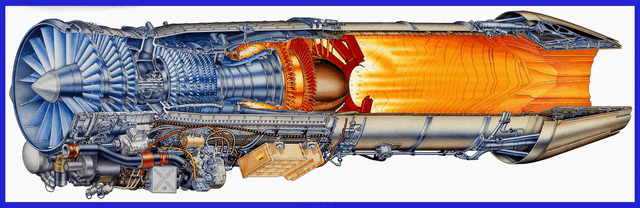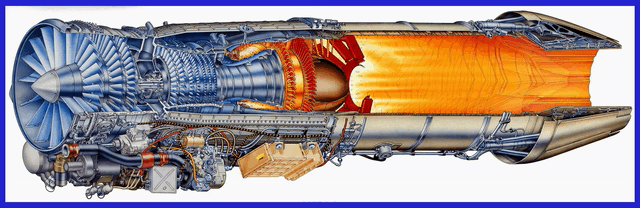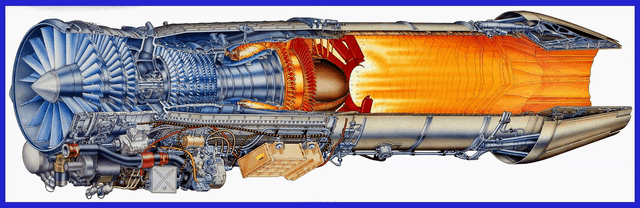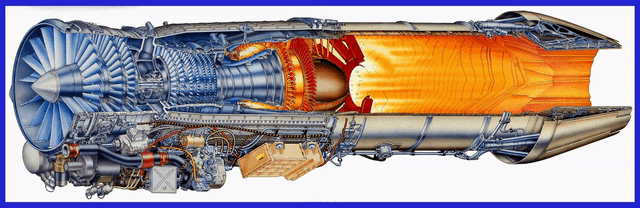
Let’s delve into the Comprehensive Details of the GE F414 and F404 Engines, with which India has proudly signed a robust contract with the esteemed American General Electric Company. With an ambitious objective in mind to meticulously engineer a cutting-edge and formidable engine, India aims to empower its upcoming Indigenous design aircraft, including the LCA MK-2, TEDBF, and AMCA, with unparalleled performance capabilities.
The GE F414 is a high-performance military turbofan engine in the 22,000-pound (98 kN) thrust with an afterburner, designed and manufactured by General Electric Aviation. It is a derivative of the successful F404 engine and has been specifically developed to power fighter aircraft, notably the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and the Saab JAS 39 Gripen NG. With its advanced design and technological enhancements, the F414 delivers increased thrust, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced performance.
Measuring approximately 154 inches (3.91 meters) in length and 35 inches (0.89 meters) in diameter, the F414 engine is a two-spool axial-flow engine featuring a high-pressure compressor, combustion system, and high-pressure turbine, as well as a low-pressure compressor and turbine. This configuration allows for efficient air intake, compression, and exhaust, resulting in optimal power generation.
One of the notable features of the F414 engine is its afterburner capability. The afterburner injects and ignites additional fuel into the exhaust stream, resulting in a significant boost in thrust during short durations, such as during takeoff or high-performance manoeuvres. This feature enhances the overall performance and manoeuvrability of the aircraft powered by the F414 engine.
The engine incorporates a Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) system, which serves as the engine’s “brain.” The FADEC system continuously monitors and controls various parameters such as fuel flow, airflow, and engine temperature, ensuring optimal performance and fuel efficiency at all times. This advanced control system allows for precise and reliable engine operation, reducing pilot workload and ensuring consistent performance.
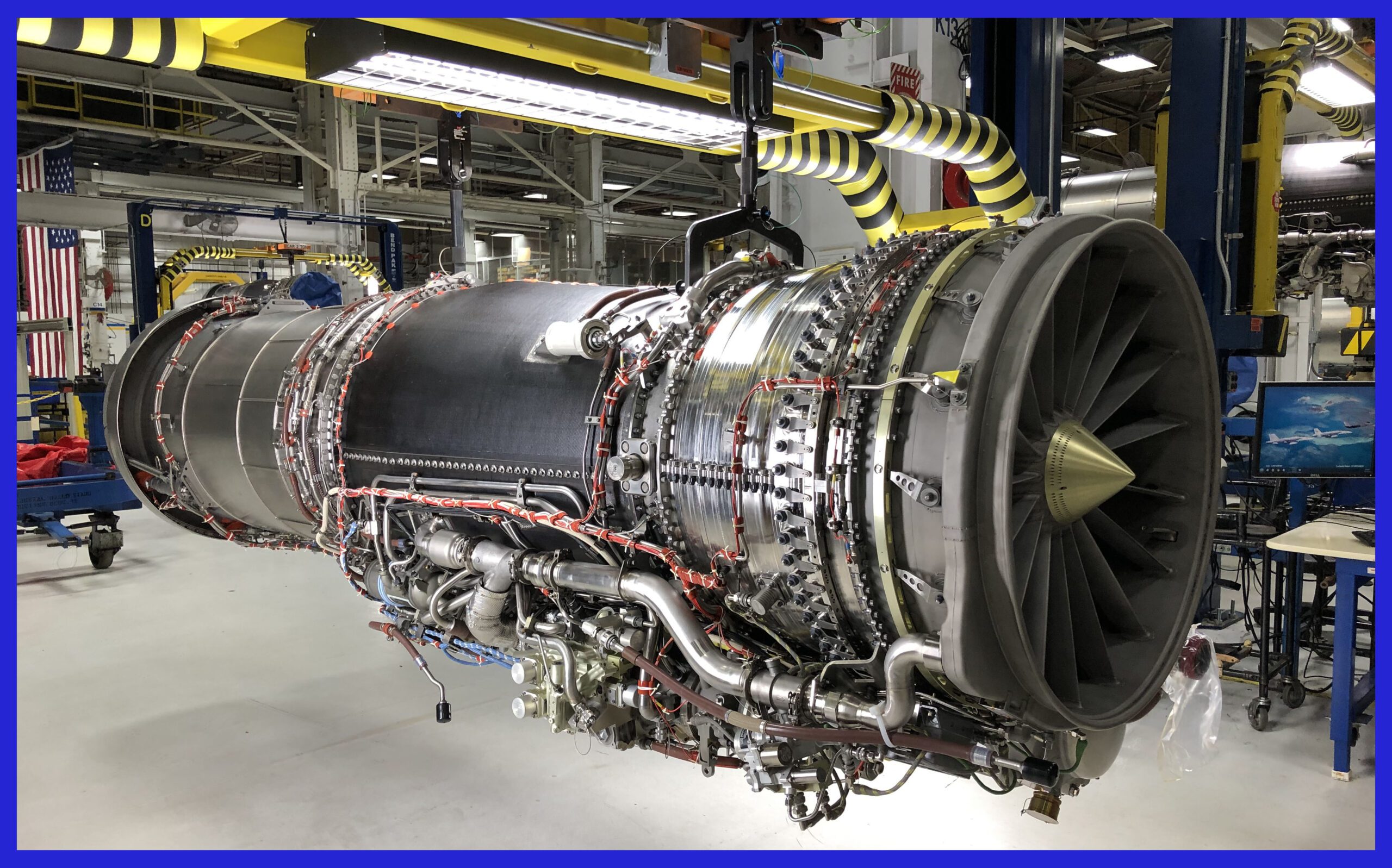
An Analysis of the General Electric F404 Engine:
The General Electric F404 engine is a widely recognized military turbofan engine that has played a significant role in powering various aircraft. Let’s delve into a detailed analysis of the engine, considering its design features, performance characteristics and notable strengths.
General Electric (GE) developed the F404 engine specifically for the F/A-18 Hornet aircraft. In the design process, the engine prioritized reliability over performance. The main objective was to achieve cost-effectiveness in its design. During the 1970s, GE conducted an analysis of “throttle profiles” and discovered that pilots were adjusting throttle settings more frequently than engineers had initially anticipated. This frequent adjustment put excessive stress on the engines. With the F404 engine, GE aimed to address these issues by creating a design that would minimize compressor stalls and other engine failures.
Additionally, the engine was intended to respond quickly to control inputs, as pilots transitioning from propeller planes to jets often complained about the lack of responsiveness in early turbojets. GE set a target for the new engine to be smaller than the GE J79 engine used in the F-4 while providing at least the same amount of thrust. Furthermore, the goal was for the F404 engine to cost half as much as the Pratt & Whitney F100 engine used in the F-16.
The F404 engine incorporates a fan that is specifically designed to ensure smooth airflow before it enters the compressor. As a result, this engine demonstrates impressive resistance to compressor stalls, even when subjected to high angles of attack. Furthermore, it exhibits exceptional responsiveness to control inputs, enabling a seamless transition from idle to full afterburner in a mere 4 seconds. To guarantee optimal performance and safety, an in-flight engine condition monitoring system (IECMS) is integrated, continuously monitoring critical malfunctions and meticulously tracking the lifetimes of various engine components.
To fulfil the Swiss Air Force’s requirement for increased power in their F/A-18 version, General Electric developed the advanced F404-GE-402 engine. This upgraded engine variant subsequently found utilization in Kuwaiti Hornets, as well as later models of the U.S. Navy’s C and D Hornets, along with subsequent variants.

The South Korean KAI T-50 Golden Eagle aircraft is equipped with a single General Electric F404-102 turbofan engine, which is accompanied by a Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) system. The engine configuration includes three-staged fans, a seven-axial stage arrangement, and an afterburner. Impressive in its capabilities, the aircraft achieves a maximum speed of Mach 1.5, while the engine generates a formidable maximum thrust of 17,700 lb (78.7 kN) when the afterburner is engaged.
General Electric (GE) has developed an upgraded version of the F404 engine specifically for Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) ‘Tejas’ aircraft, known as the F404-IN20. This particular variant represents the highest thrust version within the F404 engine family, boasting a maximum thrust of 19,000 lb (84 kN) when the afterburner is engaged. The F404-IN20 incorporates state-of-the-art advancements in hot section materials and technologies, ensuring exceptional performance and reliability.
Furthermore, it is equipped with a Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) system, which further enhances power delivery and overall engine performance. In a significant development, on 17 August 2021, India and GE finalized a contract valued at ₹5,375 crore (US$670 million). This contract entails the supply of 99 F404 engines, along with comprehensive service support, with the expected completion of delivery by 2029.
In conclusion, the General Electric F404 engine’s design, performance characteristics, applications, advancements, and notable strengths make it a highly regarded and widely utilized military turbofan engine. Its reliability, adaptability, and continuous technological improvements have solidified its position as a preferred choice for powering fighter aircraft, particularly the F/A-18 Hornet, South Korean T-50 Golden Eagle, Boeing Saab T-7 Red Hawk and HAL Tejas Mk 1/1A.
Comparative Analysis of the General Electric F414 Engine:
The Story Behind the Design Of The GE F414 Engine:
The design of the GE F414 engine traces back to the success and evolution of its predecessor, the F404 engine. In the late 1970s, General Electric developed the F404 engine for the U.S. Navy’s lightweight fighter program, which resulted in the F/A-18 Hornet. The F404 engine proved to be highly reliable and efficient, but there was a need for increased thrust and improved performance for next-generation fighter aircraft. Therefore, GE evolved the F404 into the F412-GE-400 non-afterburning turbofan for the McDonnell Douglas A-12 Avenger II aircraft, which was a proposed carrier-based stealth bomber project in the 1990s era. Unfortunately, the project was cancelled due to various internal factors.
However, the novel research conducted during that time served as a foundation for an upgraded engine for the Navy’s F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and potential use in foreign-made aircraft. GE successfully pitched the F414 as a low-risk derivative of the F404 rather than developing a completely new engine from scratch. The initial goal for the F414 engine was to utilize the same materials and processes employed in the F404, and it was designed to fit within the same footprint as its predecessor.
The design of the GE F414 engine inherits essential elements from its predecessors. It integrates the core and full-authority digital engine control (FADEC) from the F412 engine and incorporates the low-pressure system derived from the YF120 engine used in the Advanced Tactical Fighter competition. The FADEC system provided precise control over various engine parameters, such as fuel flow, compressor speed, and exhaust nozzle position. This digital control system optimized engine performance, reduced pilot workload, and enhanced overall safety and reliability.

The primary objective in designing the F414 was to provide a significant increase in thrust compared to the F404. This was achieved through the incorporation of a larger core, allowing for higher airflow and improved combustion efficiency. The engine also introduced an advanced afterburner system that injected and ignited additional fuel in the exhaust stream, generating a substantial boost in thrust when required, such as during takeoff or combat manoeuvres.
A notable difference between the F404 and the F414 is the fan section. The F414 has a larger fan than the F404 but is smaller than the F412 fan. This larger fan increases engine airflow by 16% and extends its length by 5 inches (13 cm). Accordingly, the air intake ramp of the F-18 Super Hornet has been adjusted to accommodate the larger rectangular shape.
To ensure F414 fits within the aircraft’s structure like the F404, several modifications were made. The afterburner section was shortened by 4 inches (10 cm), the combustor reduced by 1 inch (2.5 cm), and the construction of the first three stages of the high-pressure compressor now utilizes blisks instead of separate discs and dovetailed blades. These changes result in a weight reduction of approximately 50 pounds (23 kg). Furthermore, the F414 engine featured advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques, enabling higher operating temperatures and improved durability. The use of advanced alloys and coatings allowed for increased turbine temperatures, resulting in higher engine efficiency and power output. These enhancements also contributed to extending the engine’s service life and reducing maintenance requirements.
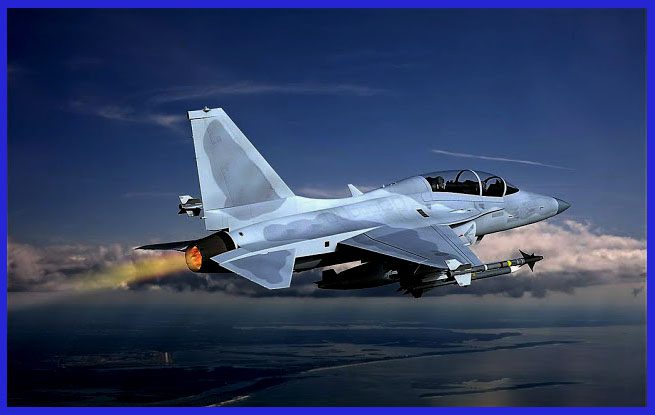

The Development of the General Electric F414 Engine:
The development of the General Electric (GE) F414 engine was primarily guided by the evolving requirements of modern fighter aircraft and the need for increased thrust, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced performance. The concept behind its development can be understood through several key factors:
Increased Thrust: As fighter aircraft became more advanced and larger, there was a growing demand for engines capable of delivering higher levels of thrust. The F414 aimed to address this need by incorporating a larger core and advanced aerodynamics to allow for increased airflow and improved combustion efficiency. These design enhancements resulted in a significant increase in thrust compared to its predecessor, the F404 engine. In 2006, General Electric (GE) tested the Enhanced Durability Engine (EDE) with an advanced core.
The EDE engine provides a 15% thrust increase or extended lifespan without additional thrust. It features a six-stage high-pressure compressor and an advanced high-pressure turbine. The turbine utilizes state-of-the-art materials and a new cooling air delivery method. Additionally, the EDE offers improved resistance to foreign object damage and reduced fuel burn rate.
Durability and Maintenance: The concept behind the F414 engine also focused on enhancing durability and reducing maintenance requirements. Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques were employed to handle higher operating temperatures and stresses, resulting in increased engine reliability and longevity. The EDE program continued by testing an advanced two-stage blade disk or “blisk” fan.
The first advanced fan was produced using traditional methods, but future blisk fans will be manufactured using translational friction welding, aiming to reduce manufacturing costs. GE asserts that this latest variant provides either a 20% increase in thrust or a threefold increase in hot-section durability compared to the current F414. This version called the Enhanced Performance Engine (EPE), received partial funding through the federal Integrated High-Performance Turbine Engine Technology (IHPTET) program. Additionally, the engine’s design incorporated modularity, enabling easier maintenance and component replacement, thereby reducing downtime and improving operational availability.
Possible F414 Improvements: Engine Noise Reduction and Emissions Control. Researchers are working on making the F414 engine better in a few ways. One way is to make it quieter by using special designs at the end of the engine called chevrons. These chevrons mix the hot air coming out of the engine with the cooler air around it, which makes the engine quieter. There are two types of chevrons: mechanical ones that look like triangular shapes and fluidic ones that use different air flows to reduce noise.
They are also trying to reduce the engine’s emissions by using a new type of combustor called a trapped vortex combustor. This combustor burns oxygen more efficiently, which means less oxygen is available to react with nitrogen and form a harmful pollutant called NOx. By burning more oxygen, the engine can produce fewer emissions. These improvements show that the F414 engine is being developed with a focus on reducing noise and making it more environmentally friendly.
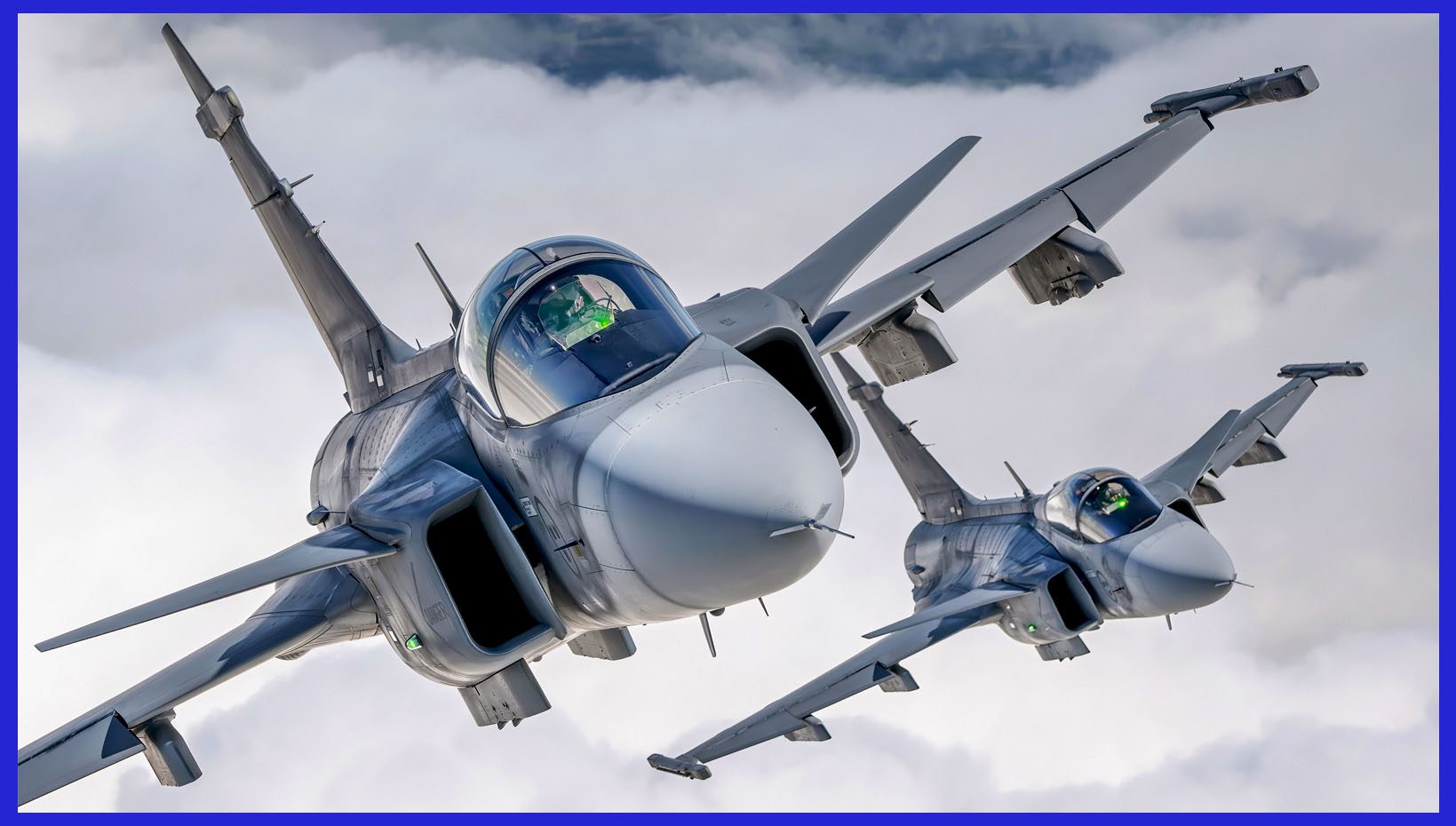

Fuel Efficiency: Another important aspect of the F414’s development was improving fuel efficiency. This was achieved through various means, including the use of advanced materials, improved aerodynamics, and enhanced combustion systems. By optimizing airflow, improving combustion efficiency, and reducing engine weight, the F414 engine offered improved fuel economy. These improvements resulted in extended range and endurance for the aircraft.
As of 2009, the F414-EDE was being developed and tested under a United States Navy contract, with the goal of demonstrating reduced specific fuel consumption (SFC) for the engine. Additionally, General Electric conducted tests on F414 engines equipped with a second low-pressure turbine stage made from ceramic matrix composites (CMC). These tests showed that CMCs are strong enough to withstand the heat and stress inside the turbine. The advantage of CMCs is that they weigh only one-third as much as metal alloys and can operate without the need for cooling air. This makes the engine more aerodynamically and fuel efficient.
Customer-Specific Requirements: When developing the F414 engine, GE also took into consideration the specific requirements of customer nations. They created variants such as the F414-GE-400K and F414-GE-INS6 to meet the specific needs of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) HAL Tejas Mark 2 aircraft. In October 2010, India placed an order for 99 engines. Similar variants were developed for the South Korean KAI T-50 Golden Eagle and KF-X fighter aircraft projects. This customer-centric approach allowed for tailored solutions that could fulfil the unique performance objectives of these programs. The engine produces more thrust compared to previous versions and incorporates a Full Authority Digital Electronics Control (FADEC) system.
Overall, the concept behind the development of the GE F414 engine revolved around meeting the increasing demands of modern fighter aircraft. By focusing on increased thrust, improved fuel efficiency, durability, and advanced control systems, the F414 engine delivers enhanced performance and operational capabilities for next-generation fighter platforms.
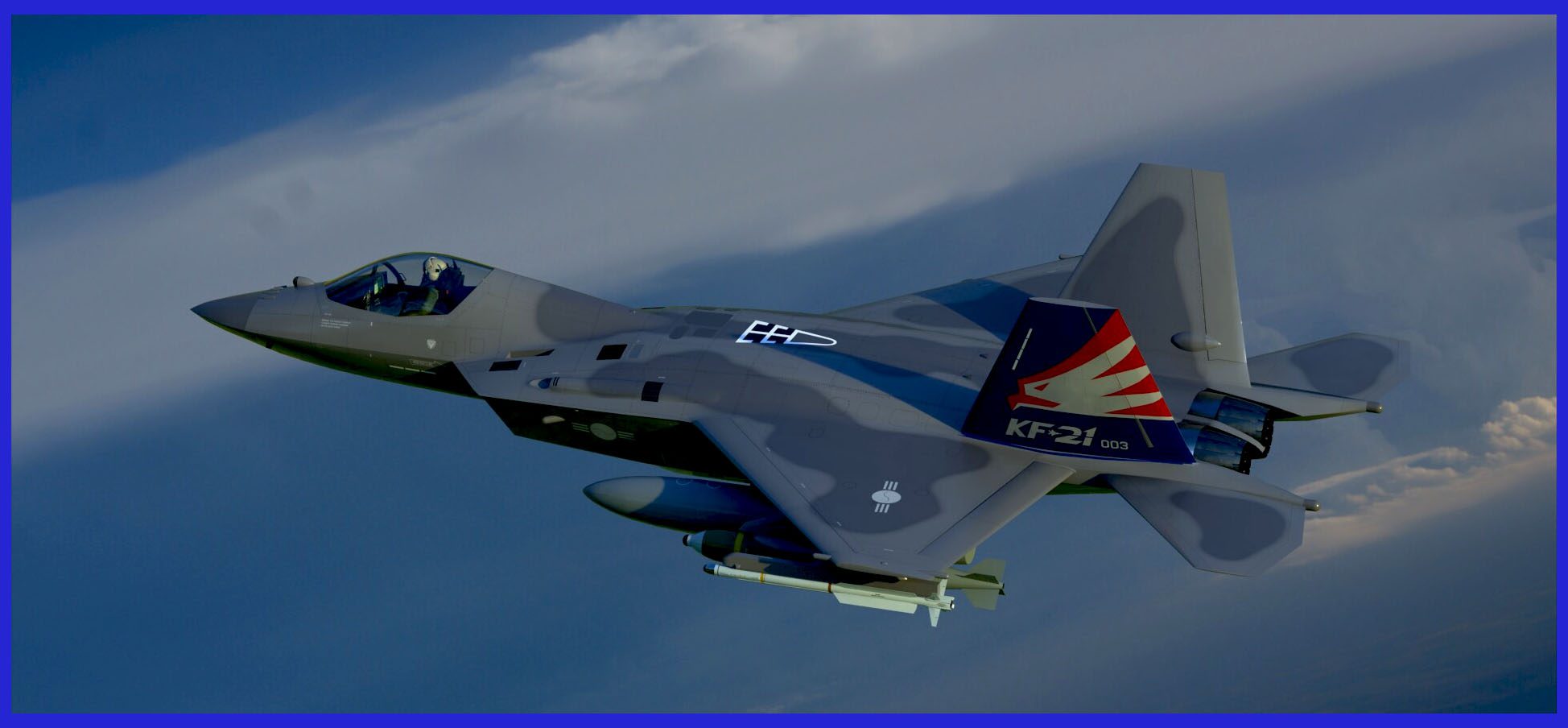

Variants Of The General Electric F414 Engine as of 2023:
Here are some of the known variants of the General Electric F414 engine
- F414-GE-400: This is the initial production variant of the F414 engine. It powers the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet aircraft.
- F414-EDE: An enhanced high-pressure turbine (HPT) and high-pressure compressor (HPC) are components of the Enhanced Durability Engine (EDE). The HPT has undergone aerodynamic improvements and has been developed to endure somewhat greater temperatures. The HPC was revamped, going from 7 stages to 6. These modifications were made to lower specific fuel consumption (SFC) and increase component durability by three times.
- F414-EPE: New core, fan, and compressor are all parts of the Enhanced Performance Engine (EPE). provides a 20 percent thrust boost, increasing it to 26,400 lbf (117 kN), for a thrust-to-weight ratio of almost 11:1.
- F414M: utilized by EADS Mako/HEAT. The derated thrust of 12,500 pounds dry and 16,850 pounds wet, or 55,6 and 75 kN, respectively. proposed for the international T-50 series of Korean trainers and fighters, but was later supplanted by a new offer using a standard F414.
- F414-G: For the Saab JAS 39 Gripen Demonstrator, F414-G was produced. used in a single-engine Gripen rather than a twin-engine aircraft like the F/A-18 after being slightly modified. With it, the Gripen Demonstrator (without afterburners) accelerated to Mach 1.2.
- F414-GE-INS6: The F414-GE-INS6 was chosen by India’s Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) to power the HAL Tejas Mark 1 and 2 of the Indian Air Force (IAF). 99 engines were ordered by India in October 2010. In addition to having a Full Authority Digital Electronics Control (FADEC) system, it delivers more thrust than prior iterations. By 2013, the engines must be delivered.
- F414-GE-39E (GE RM16): For the Swedish Saab JAS-39E/F Gripen, a new version of the F414G is available.
- F414-GE-400K: A variant of the F414-GE-400, co-developed by General Electric and Hanwha Aerospace, has been designed for the South Korean KAI KF-21 Boramae. This variant is set to be manufactured jointly and assembled locally in South Korea by Hanwha Aerospace.
- F414-GE-100: A version specifically custom-made to drive NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane has been developed. This version is derived from the F414-GE-39E and incorporates several modifications, including different control software, fuel piping, and the absence of mounting rails. It is noteworthy that two units of this custom-made version have been produced.

Technical Specifications of the General Electric F404 and F414 Engines:
- Type: Afterburning capable turbofan engine
- Length: 154 in (391 cm)
- Diameter: 35 in (89 cm)
- Dry weight: F404_ 1,035 kg (2,282 lb) and F414_ 1,110 kg (2,445 lb ) max weight
- Compressor: axial compressor with 3 low-pressure stages and 7 high-pressure stages
- Combustors: annular type
- Turbine: 1 low-pressure(LP) stage and 1 high-pressure stage(HP)
- Maximum thrust: For the F404 engine is 11,000 lbf (48.9 kN) in military thrust and 17,700 lbf (78.7 kN) with an afterburner, whereas for the F414 engine, it is 13,000 lbf (57.8 kN) in military thrust and 22,000 lbf (97.9 kN) with afterburner
- Overall pressure ratio: is 26:1 for the F404 engine and 30:1 for the F414 engine
- Bypass ratio: for the F404 engine is 0.34:1, while for the F414 engine, it is 0.25:1
- Air mass flow: for the F404 engine is 66 kg/s (146 lb/s), while for the F414 engine, it is 77.1 kg/s (170 lb/s)
- Thrust-to-weight ratio: for the F404 engine is estimated to be 4.8 (dry) and 7.8 (afterburning), while for the F414 engine, it is estimated to be 5.9 (dry) and 9 (afterburning).

However, do not miss out on the extraordinary chance to own an exquisite collection of exclusive 1/72 premium diecast scale models that showcase the legendary McDonnell Douglas/Boeing F/A-18F Super Hornet. These awe-inspiring models capture the essence and beauty of this iconic aircraft, enabling you to admire its sleek design and remarkable details up close. Whether you are a passionate aviation enthusiast or a collector in search of unique pieces, this collection is a must-have, providing a rare opportunity to possess a piece of aviation history.
In conclusion, the General Electric F414 engine stands as an immensely powerful and remarkably versatile military turbofan engine that has unequivocally demonstrated its exceptional capabilities in a wide array of high-performance aircraft. With its cutting-edge design, awe-inspiring thrust capabilities, and relentless advancements, the F414 engine has firmly established itself as an unwaveringly dependable and highly coveted choice for contemporary combat aircraft.
The F414 engine encompasses an extensive range of variants meticulously tailored to meet precise operational requirements. From propelling the Boeing F/A-18 Super Hornet series, encompassing the Block II and Block III variants, to empowering the Saab Gripen NG and HAL Tejas aircraft, each variant has been painstakingly optimized to deliver unparalleled performance, exceptional fuel efficiency, and manageable maintenance demands.
Bearing in mind these remarkable and superior characteristics inherent in this esteemed and standard-configured engine, it is worth noting that today ( while writing this article), on the 22nd of June 2023, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi embarks on an official visit to the United States of America. Amongst the various agreements and collaborations between these two nations, India will enter into a contract with General Electric to manufacture the most cutting-edge version of the F-414 engine, which will propel the indigenous future projects of LCA Tejas Mk-II, TEDBF, and AMCA (5th Gen) aircraft.
With an optimistic outlook, it is hoped that the resulting agreement will benefit both nations and foster the development of military ties, ultimately bolstering the quality of future military accomplishments. As technology continues to advance and new aircraft requirements emerge, the General Electric F414 engine perseveres in its evolution, relentlessly pushing the boundaries of performance and efficiency. It remains an indispensable component of modern military aviation, actively contributing to the success of combat missions and ensuring the unwavering preparedness of the aircraft it propels.

Important Announcement for Our Valued Readers!
After an article is published, it is possible that updates or changes may have occurred beyond the time of publication. Therefore, it is important to be aware that certain information in the article might be outdated. To ensure the most accurate analysis, it is highly recommended to verify the content with the latest sources available.
However, we are dedicated to delivering outstanding articles on military products and global updates. Maintaining quality and smooth operation requires resources. Your support sustains our efforts in providing insightful content. By purchasing high-quality products through our affiliated links, you help us keep our platform alive and acquire top-notch items. Your unwavering support is invaluable and inspires us to strive further.
We welcome your suggestions and requests for more information, as we value feedback from our readers. If there’s specific defence material or equipment not covered on our site, please share your request in the comments. We’ll strive to research and provide the required information. We sincerely thank you for your unwavering interest in our website, and we eagerly anticipate hearing from you! Enjoy your reading experience!