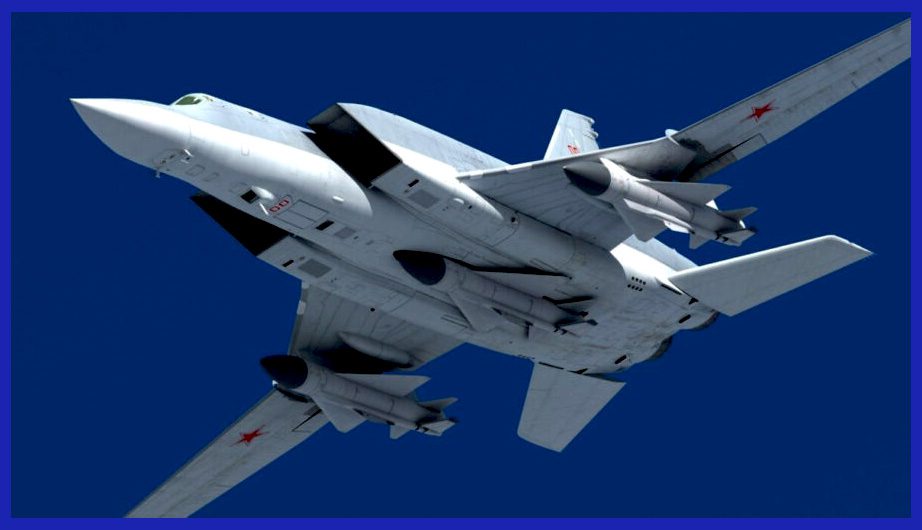
During its heyday, the Kh-22 missile was an unparalleled force to be reckoned with, striking fear into the hearts of potential adversaries. Let’s Explore The Details Of The Massive Kh-22 Missile, which is a formidable, long-range supersonic weapon developed during the Cold War by the Soviet Union. Primarily designed for engaging and obliterating enemy ships, particularly aircraft carriers, the Kh-22 possesses astounding speed, extensive range, and devastating capabilities. With its imposing size and weight, the missile can deliver a high-explosive or nuclear warhead to targets up to 600 km away.
Despite its limited operational use, the Kh-22 played a vital role in the Soviet arsenal during the 1980s. Subsequently, it underwent a complete transformation into the Kh-32 configuration in response to NATO’s missile advancements. Consequently, the Kh-32 emerged as Russia’s supremely powerful supersonic air-launched cruise missile, boasting a remarkable range of 1000 km.

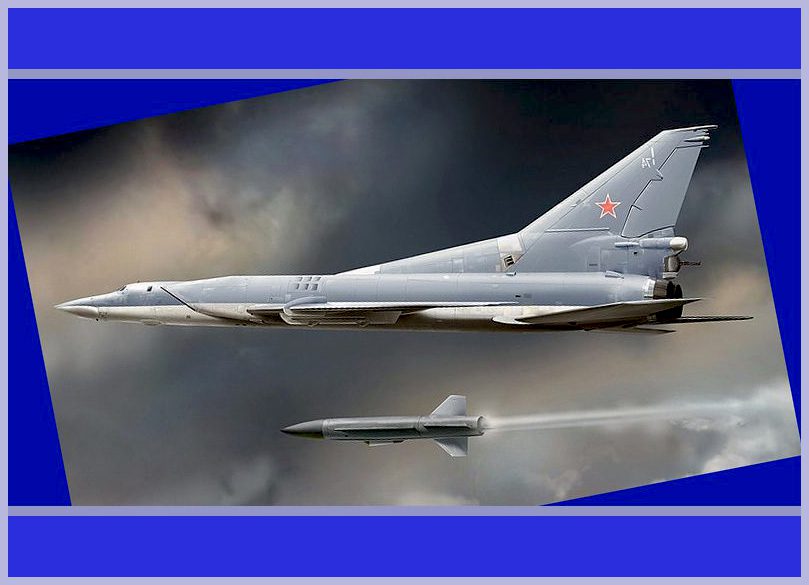
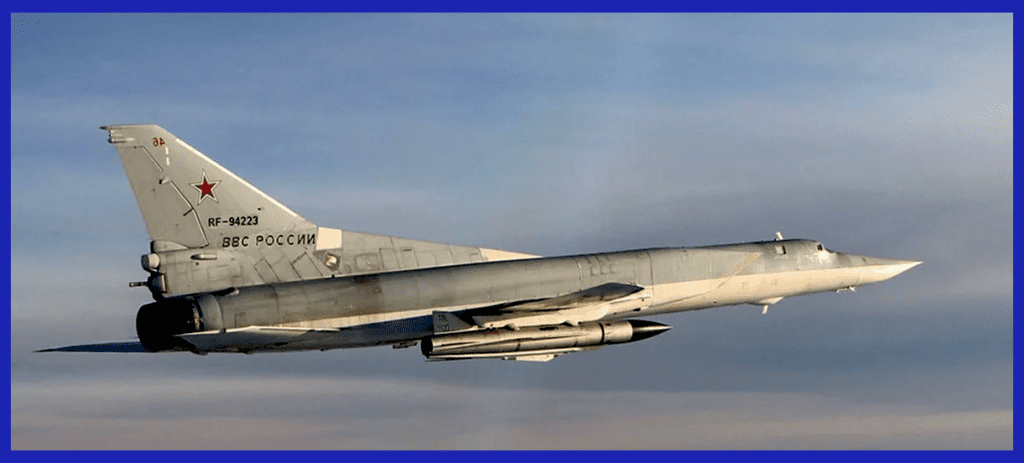
The NATO-designated name for the missile is “Kitchen,” while it is commonly known as the Kh-32. This particular missile represents a highly anticipated upgrade over its predecessor, the Kh-22, and it comes in both conventional and nuclear variants. Officially introduced into service in 2016, the Kh-32 boasts numerous improvements, including a more advanced rocket motor and an upgraded seeker head, both of which were developed by the renowned MKB Raduga. Specifically designed for use on Tu-22M3M bombers, the Kh-32 stands out for its remarkable advancements in capability and technology. Its integration into active service signifies a significant milestone in the ongoing development of supersonic weaponry.

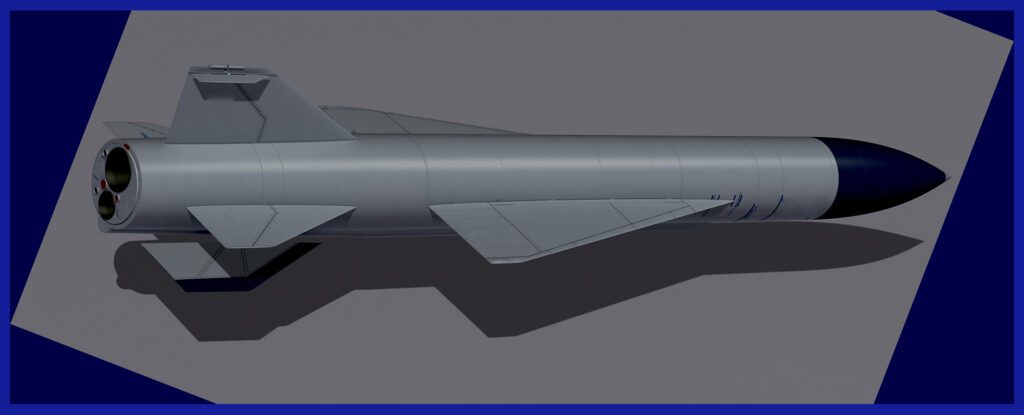
Analyzing The Design Of The Kh-22 Kitchen ASM
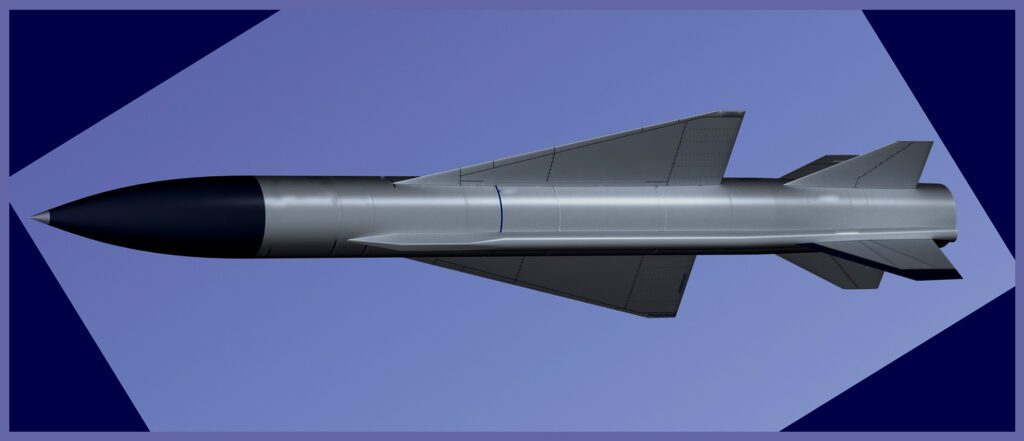
The design of the Kh-22 Kitchen ASM ( Air-Surface Missile ) was a remarkable achievement during its time. Its slender and elongated airframe, approximately 11.6 meters in length, featured a streamlined shape that minimized aerodynamic drag. The missile was propelled by a powerful Tumansky liquid-fuel rocket engine, enabling it to reach high speeds of Mach 4 to Mach 5.
With a range of up to 600 kilometres, the Kh-22 could engage targets from a significant distance. It offered versatility through different warhead options, including high-explosive and nuclear variants, with the latter possessing a yield of up to 1 megaton. Additionally, it could be launched in either high-altitude or low-altitude mode.
In the high-altitude mode, it would climb to an altitude of 27,000 meters ( 89,000 feet ) and make a high-speed dive into the target, achieving a terminal speed of about Mach 4.6. In the low-altitude mode, it would climb to 12,000 meters ( 39,000 feet ) and execute a shallow dive at approximately Mach 3.5. The missile’s guidance was facilitated by a gyroscope-stabilized autopilot working in conjunction with a radio altimeter.
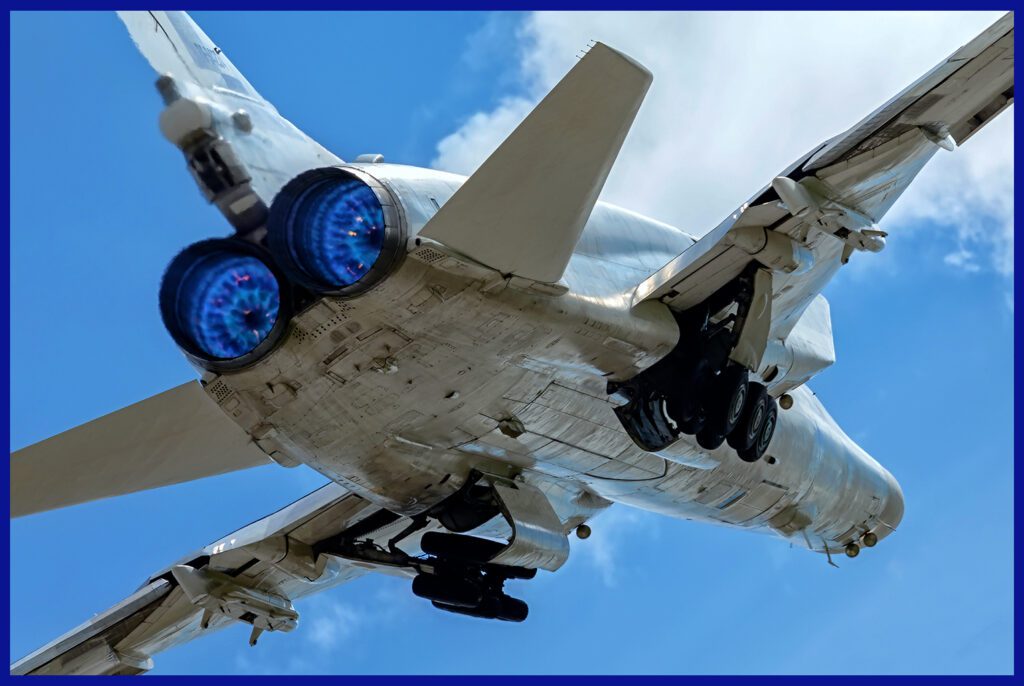

The Kh-22 employed an advanced guidance system that utilized inertial navigation and terminal homing to ensure accurate targeting. It was adaptable to various launch platforms, including bombers like the Tu-22 and Tu-95, as well as the MiG-31. During tests, it was revealed that when a shaped charge warhead weighing 1,000 kg ( 2,200 lb ) was used, the resulting hole measured 5 meters ( 16 feet ) in diameter, covering an area of 19.6 square meters (210 square feet) and reaching a depth of 12 meters ( 40 feet ).
The missile also incorporated countermeasures, such as chaff, flares, and electronic countermeasures, to effectively evade enemy air defences. Overall, the Kh-22’s design encompassed advanced aerodynamics, powerful propulsion, precise guidance, and the ability to carry different warheads, making it a formidable anti-ship missile.

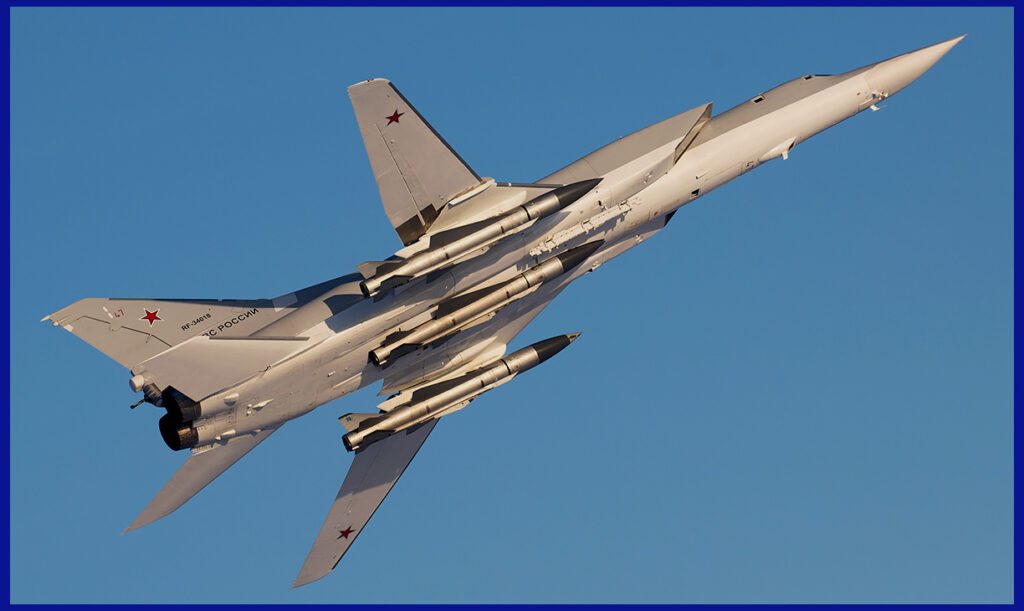
The Next-Generation Kh-32 ASM: Key Differences From The Kh-22
In August 2016, Russia was in the final stages of conducting trials for the Kh-32 cruise missile, which is a modified version of the Kh-22 Kitchen missile. This particular missile was specifically designed to be used with the Tu-22M3 bomber. Upon launch, the missile’s intended trajectory involves climbing to an altitude of 40 km (130,000 ft) in the stratosphere, transitioning to level flight, and then executing a steep dive towards its target, such as aircraft carriers. Additionally, the cruise missile variant is optimized for engaging smaller enemy vessels, radar installations, and “radio-contrast targets” like bridges, military bases, and electric power plants, among others.
The Kh-32 cruise missile is equipped with an autonomous inertial navigation system and a radar homing head, allowing it to operate independently without relying on GPS/GLONASS navigation satellites. This sophisticated missile is estimated to have a range of approximately 1,000 km (620 mi) and can achieve impressive speeds of at least 5,000 km/h (3,100 mph; Mach 4.1). It became operational in the same year it was introduced. According to reports, a total of thirty-two Kh-22 missiles were successfully upgraded to the Kh-32 level between 2018 and 2020.
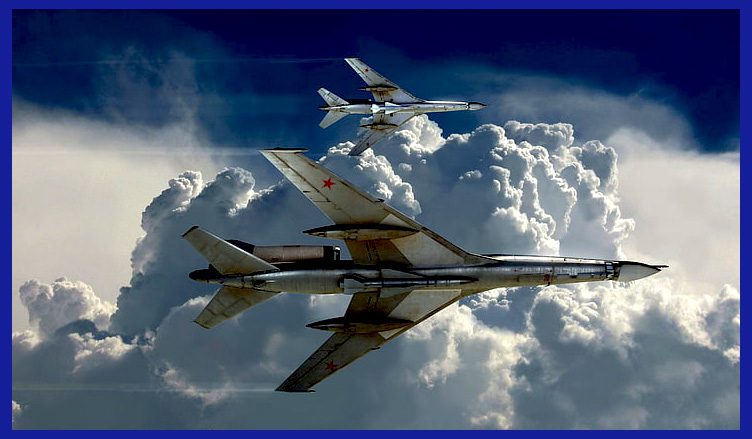

Airframe: The Kh-32 features a slender, elongated airframe measuring approximately 11.6 meters in length. Its design incorporates a streamlined shape to minimize aerodynamic drag and maximize its speed potential. The Kh-32 missile is manufactured using the Kh-22 case, and its geometrical dimensions are entirely identical. The warhead weight has been reduced to 500 kg ( 1,100 lb ) in order to enhance the range.
Range and Speed: The Kh-32 boasts an impressive operational range of up to 1000 kilometres, allowing it to engage targets from a significant distance. This means it can be launched outside the maximum range of US Navy F/A-18 Super Hornets, which have a combat radius of around 885 kilometres. Additionally, its supersonic speed capabilities, ranging from Mach 4 to 5, ensure swift delivery to the target, significantly reducing the chances of interception.

Launch Platforms: The Kh-32 was originally designed to be launched by Russian bombers, such as the Tu-22 and Tu-95. Later versions were adapted for use with other aircraft, including the MiG-31. This versatility allowed the missile to be deployed from various platforms.
Countermeasures: To enhance its survivability, the Kh-32 was equipped with countermeasures to evade enemy air defences. These countermeasures included chaff, flares, and electronic countermeasures to disrupt enemy radar systems.
Reliability: The Kh-32 is known for its robust design and reliability, allowing it to withstand the harsh conditions of supersonic flight and ensure mission success.
Overall, the design of the Kh-32 Kitchen ASM encompassed advanced aerodynamics, powerful propulsion, accurate guidance systems, and the capability to carry different warhead types. These features combined to create a formidable missile capable of engaging enemy ships at long ranges and posing a significant threat to naval forces.

The Concept Behind The Development Of The Kh-22 Kitchen ASM
After analyzing naval battles and encounters during World War II and the late 1940s to early 1950s, Soviet military strategists reached the conclusion that the era of large-scale naval engagements was coming to an end. They recognized that stand-off attacks using cruise missiles would be an effective way to neutralize and incapacitate enemy battle groups without having to deploy a comparable force.
As a result, the Soviet Air Forces and Soviet Naval Aviation commanders embarked on the task of converting their heavy bombers into missile carriers, capable of launching attacks against approaching enemy fleets from coastal or island airfields. The Kh-22 weapon was developed by the Raduga design bureau based on this strategy and was specifically intended for arming the Tupolev Tu-22M aircraft for this purpose.
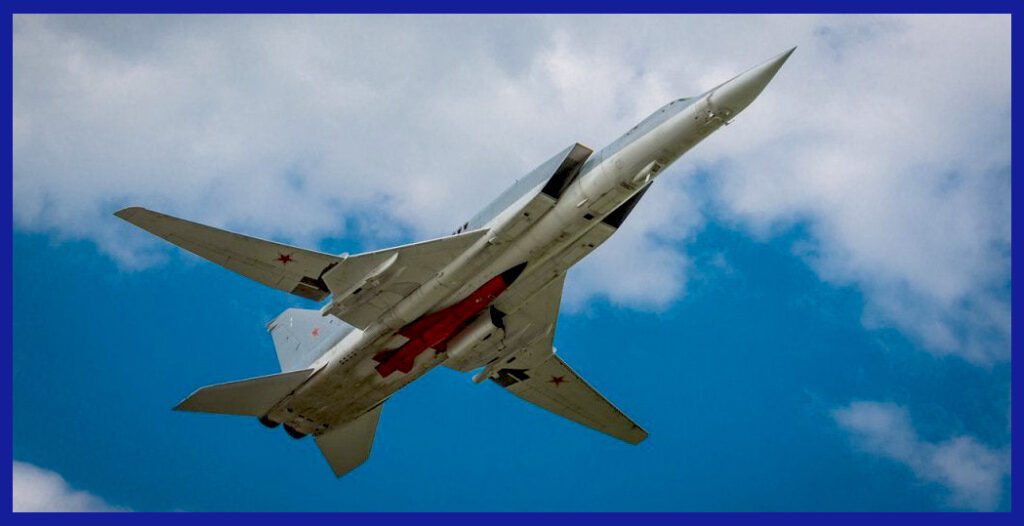

The specifically designed Kh-22 Kitchen ASM was driven by the concept of creating a powerful, long-range anti-ship missile to counter the threat posed by enemy naval forces, particularly aircraft carriers. The Soviet Union recognized the need for a weapon system that could effectively engage and neutralize large surface vessels, which were considered critical components of the enemy’s naval power projection.
Presently the primary objective of the Kh-22 and Kh-32 development was to provide the Russian Air Force and Navy with a formidable weapon capable of striking targets at extended ranges. The missile needed to possess high speed, long-range capability, and a potent warhead to ensure a high probability of successfully disabling or destroying enemy ships.
By incorporating advanced aerodynamics and propulsion systems, the Kh-22 and Kh-32 aimed to achieve supersonic speeds, allowing them to rapidly close the distance to their target and reduce the time available for enemy defences to react. The missile’s streamlined airframe minimized aerodynamic drag, enabling efficient and swift flight.
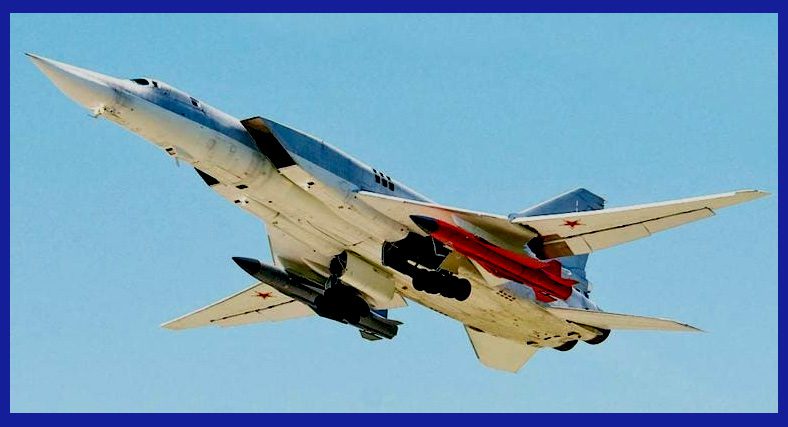

The Kh-22 Kitchen: History Of Operations
Although the Kh-22 missile was introduced into the Russian arsenal during the Soviet era in the 1980s, its actual usage came into effect in the ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine. The first reported combat use of the missile occurred on May 11, 2022, when a video surfaced on the internet showing a Russian Air Force Tu-22M3 strategic bomber launching a pair of Kh-22 or Kh-32 missiles at targets located somewhere in Ukraine.
On May 9, 2022, reports emerged stating that the Russian Air Force fired 13 Kh-22 missiles. Seven of these missiles were targeted at Fontanka, a coastal village located approximately 15 km north of Odesa. One of the missiles struck the Riviera shopping mall in the vicinity.
On June 27, 2022, two Kh-22 or Kh-32 missiles were reportedly launched by Russian Tupolev Tu-22M3 bombers in the Kremenchuk shopping mall attack. The attack resulted in the death of at least 21 people and injured at least 59. One missile directly hit the mall, while the other fell approximately 450 meters away, near the edge of the Kredmash Road Machinery Plant.
Since the beginning of the war until May 2023, it is estimated that around 40 older versions of the Kh-22 missile were used on land-based targets in Ukraine, depleting the existing stocks of the missile from the Russian inventory.

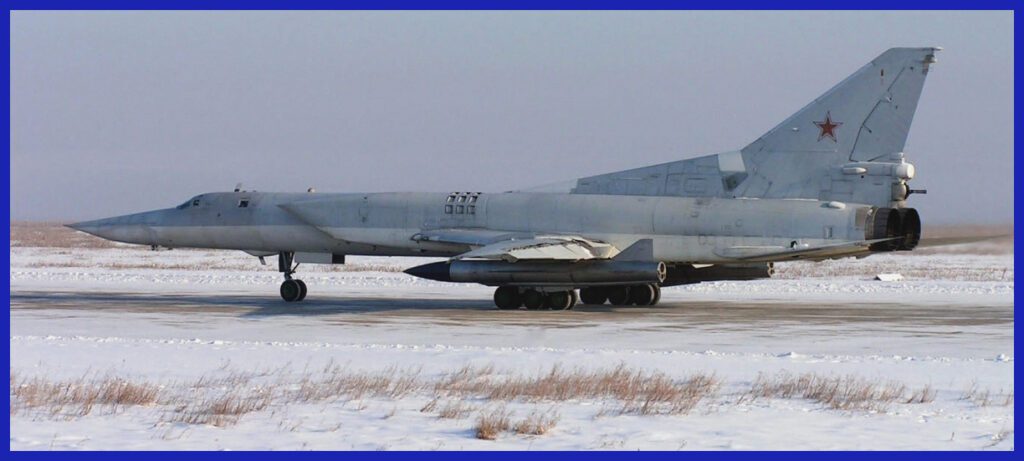
The Kh-22 / Kh-32 Kitchen Technical Specifications
- Weight: 5,820 kg ( 12,800 lb )
- Length: 38.2 ft ( 11.65 m )
- Diameter: 3 ft ( 36 in )
- Wingspan: 10 ft ( 120 inch )
- Warhead: Kh-22: Conventional ( RDX ) or Thermonuclear warhead, weighing 1000 kg / Kh-32: 500 kg
- Engine: Liquid-fuel rocket
- Operational Range: Kh-22: 600 km / Kh-32: Max 1,000 km
- Speed: Maximum Mach 4.6
- Accuracy: 80 to 250 m CEP ( Circular Error Probable )
- Guidance: Inertial guidance followed by terminal active radar homing
- Launch Platform: Only designed for Russian aircraft, which include: Tu-22M3M, Tu-95K and MiG-31

Furthermore, it is important to highlight that you now have the extraordinary opportunity to acquire remarkable scale models of the Su-30 and MiG-29 fighter jets, conveniently available on Amazon and Air Models. For those interested in military history, there is also a thrilling book on the Tupolev Tu-22M Bomber available for purchase on Amazon. This weapon system, renowned for its devastating capabilities demonstrated on the battlefield, serves as a testament to the unwavering dedication of the Russian military to advanced technology and precision warfare. Get it now to secure your piece before the limited stock is depleted.

In conclusion, the Kh-22 Kitchen ASM stands as a formidable testament to the ingenuity and technological prowess of its era. With its sleek design, blazing speed, and devastating firepower, the Kh-22 emerged as a symbol of power projection and naval deterrence. Its primary purpose was to engage and obliterate enemy vessels from afar, harnessing supersonic might and precise guidance to strike fear into the hearts of adversaries.
Despite its operational history remaining veiled in secrecy, the mere presence of the Kh-22 evoked a sense of awe and respect on the battlefield. Even as newer anti-ship missile systems emerged with the tides of progress, the legacy of the Kh-22 endures, serving as a reminder of its reign as a true titan among weapons of its time.

Important Announcement for Our Valued Readers!
After an article is published, it is possible that updates or changes may have occurred beyond the time of publication. Therefore, it is important to be aware that certain information in the article might be outdated. To ensure the most accurate analysis, it is highly recommended to verify the content with the latest sources available.
However, we are dedicated to delivering outstanding articles on military products and global updates. Maintaining quality and smooth operation requires resources. Your support sustains our efforts in providing insightful content. By purchasing high-quality products through our affiliated links, you help us keep our platform alive and acquire top-notch items. Your unwavering support is invaluable and inspires us to strive further.
We welcome your suggestions and requests for more information, as we value feedback from our readers. If there’s specific defence material or equipment not covered on our site, please share your request in the comments. We’ll strive to research and provide the required information. We sincerely thank you for your unwavering interest in our website, and we eagerly anticipate hearing from you! Enjoy your reading experience!

