Setting forth on this cosmic expedition, we delve into the universe’s mysteries, unveiling the enigmas of our Sun and the myriad worlds that encircle it. Let’s Explore Our Sun And All The Planets; through this exploration, we can glean insights into the origins of our solar system, the distinct physical properties of each planet, and even the tantalizing prospect of discovering life beyond Earth!! Each planet embodies unique characteristics and features that set them apart.
However, the Earth, characterized by its intricate balance and supportive ecosystem, remains unmatched as the ultimate sanctuary for human dwelling and life as comprehended by us. Acting as the gravitational focal point, the Sun assumes the role of the central star within our solar system, exerting its influence as it governs the orbital paths of all the planets that revolve around it.

The Basic Knowledge Of Our Sun
The Sun is a star. It is a huge burning ball of gas at the centre of the solar system. All planets ( including the Earth and celestial bodies in the solar system ), orbit around the Sun. The Sun has formed about 4.6 billion years ago.
The Sun is a massive, luminous ball of gas that is the central star of our solar system. It is classified as a G-type main-sequence star, with a surface temperature of about 5,500 degrees Celsius ( 9,932 degrees Fahrenheit ) and a diameter of approximately 1,392,000 kilometres ( 864,938 miles ). The Sun’s energy is generated through nuclear fusion reactions that occur in its core, which produces heat and light that sustain life on Earth. This is 109 times the diameter of the Earth. The Sun is so large that we could fit over one million Earths inside of it.
The Sun also has a strong magnetic field that creates sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections, which can affect the Earth’s climate and technology. Understanding the basic properties and behaviour of the Sun is important for studying the solar system, space weather, and the potential for life beyond Earth.
It takes about 8 minutes and 20 seconds for the Sun’s light to reach the Earth, travelling at a speed of about 299,792 kilometres per second ( 186,282 miles per second ).
Looking directly at the Sun can cause permanent eye damage, so it’s important to use special filters or viewing equipment when observing it.

How Hot Is The Sun? _ The Sun is very Hot. The temperature at the centre or core is over 15,000,000 degrees Celsius ( 27,000,32 degrees Fahrenheit ). The Sun gives us light and warmth which are extremely important for life. Without the Sun, the Earth would be a dark and frozen ball.
What Is A Sunspot? _ Sunspots are temporary dark spots on the surface of the Sun. Sunspots appear dark because they are cooler than the surrounding regions. Sunspots are large enough to be seen with the naked eye. The largest Sunspots have a diameter of 50,000 kilometres ( about 31,069 miles )
What Are Solar Flares? _ Solar flares are powerful and brief eruptions of energy that occur on the surface of the Sun, releasing a burst of high-energy radiation into space. They are typically associated with sunspots and can affect various aspects of technology and communication on Earth.
What Are Coronal Mass Ejections? _ Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are massive and powerful eruptions of plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun’s corona into space. They can release billions of tons of matter at speeds of millions of miles per hour and interact with Earth’s magnetic field, potentially causing geomagnetic storms and other space weather effects.
What Do You Understand About ” Sun Is A Massive, Luminous Ball Of Gas? “ _ means that the Sun is a celestial body that is made up of extremely hot and dense gases, primarily hydrogen and helium. It emits a large amount of energy and light due to the nuclear fusion reactions that occur at its core, which convert hydrogen into helium. The Sun is considered massive because it contains about 99.86% of the total mass in our solar system.
A Few Facts _
- The burning of hydrogen with helium in the Sun’s core makes it shine brightly.
- Many Sunspots are equal to the size of the Earth
- The Sun is the closest star to Earth and is located at the centre of the solar system.
- The Sun’s energy output is about 386 billion megawatts, which is equivalent to the energy produced by about 100 billion tons of TNT exploding every second.
What Do You Know About The Stars And Constellations?
Stars are huge, brightly shining balls of hot gases in space. Stars give off light and other forms of energy. Stars are found in galaxies. About 75% of stars are found in pairs. A group of stars in a region of the night sky forms a constellation. Until now, 88 constellations have been spotted and named.
The positions and shapes of stars and constellations change over time due to their motion in space and the Earth’s rotation, which causes them to appear to move across the sky over the course of a night.
Names Of Constellations _ Constellations are named after different animals and mythological characters. For example, the cancellation Leo is named after a Lion and the Constellation Orion is named after a Greek mythological character.
There are 88 officially recognized constellations, which are divided into both the northern and southern hemispheres of the sky. Here are some of the most well-known constellations:
- Orion
- Ursa Major (Great Bear or Big Dipper)
- Ursa Minor (Little Bear or Little Dipper)
- Cassiopeia
- Leo
- Gemini
- Scorpius
- Sagittarius
- Taurus
- Canis Major (Greater Dog)
- Canis Minor (Lesser Dog)
- Cygnus (the Swan)
- Aquila (the Eagle)
- Pisces
- Aries
- Virgo
- Capricornus
- Andromeda
These constellations have been recognized for thousands of years and were originally used for navigation, storytelling, and tracking the changing seasons.

Stars Life Cycle _ Stars are not permanent objects that twinkle in the sky. They have a life. They are born, grow and age and then die. The different phases of a star’s life cycle are– protostar, main sequence star, red giant, white dwarf, black dwarf and supernova.
The exact stages depend on the mass of the star, with more massive stars undergoing more complex and explosive phases. The life cycle of a star can take millions or billions of years to complete, and each stage is characterized by different physical and chemical processes occurring within the star. A protostar is the earliest phase of the star. When the close of a protostar becomes very hot and dense, a main sequence star is formed. Main sequence stars burn hydrogen to form helium. They are the most luminous stars.
Our Sun is a main sequence star. After burning hydrogen for millions of years main sequence stars that are the size of our Sun, transform into red giants. Red giants lose their brightness and end up as white dwarfs. Stars that are bigger than our Sun end their lives in a huge explosion known as supernovae.
A Few Facts _
- Some constellations can be seen only during certain seasons due to the earth’s revolution.
- All constellations can be viewed from the equator during the course of the year.
- On a starry night, we can see about 3,000 stars.
What Do You Know About Inner Planets?
Our solar system has eight planets. All of the planets revolve around the Sun, which is at the centre of the solar system. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are the planets closest to the Sun. They are called the inner planets. They are small in size and are mainly made of rock.
- They are all terrestrial planets, meaning they are primarily composed of rock and metal.
- They have shorter orbital periods and are closer to the Sun than the outer planets.
- Mercury is the smallest and closest planet to the Sun, while Mars is the largest and farthest of the inner planets.
- Earth is the only planet known to support life.
- Venus has the hottest surface temperature of any planet in the solar system due to its thick, carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere.
- Mars has the largest volcano (Olympus Mons) and the deepest canyon (Valles Marineris) in the solar system.

The Planet Mercury: Mercury is the closest and smallest planet to the Sun. It travels around the Sun faster than any other planet. It takes only 88 days to orbit around the Sun. It has a diameter of just 4,880 kilometres, which is about one-third the size of Earth. Due to its proximity to the Sun, temperatures on Mercury can reach over 800 degrees Fahrenheit (427 degrees Celsius) during the day, while dropping to -290 degrees Fahrenheit (-180 degrees Celsius) at night.
Mercury has a heavily cratered surface, and its thin atmosphere is composed primarily of helium and hydrogen. It has no moons and completes three rotations for every two orbits around the Sun, which means that a day on Mercury (the time it takes to rotate once) is longer than a year on Mercury (the time it takes to orbit the Sun once). Mercury has been explored by a number of spacecraft, including NASA’s Mariner 10 and MESSENGER missions.
The Planet Venus: Venus is the second planet from the Sun and the closest to the Earth. It is the brightest of all planets. Venus is covered with a sheet of thick clouds, which holds all of the heat and makes it very hot. It has a diameter of 12,104 kilometres, which is approximately 95% the size of Earth. Venus is known for its thick, toxic atmosphere, which is composed mainly of carbon dioxide and has a surface pressure about 90 times that of Earth’s atmosphere.
This dense atmosphere creates a strong greenhouse effect, trapping heat and making Venus the hottest planet in the solar system, with surface temperatures that can exceed 870 degrees Fahrenheit (465 degrees Celsius). Venus also has a retrograde rotation, meaning it rotates on its axis in the opposite direction to the other planets, and it does not have any moons. The planet has been visited by a number of spacecraft, including NASA’s Pioneer and Magellan missions.
The Planet Earth: Earth is the third planet from the Sun. It is the only planet known to support life. About 71% of the earth’s surface is covered with water. The optimum distance from the Sun and a favourable atmosphere are two factors that make life possible on Earth. It has a diameter of 12,742 kilometres and is the fifth largest planet in our solar system. Earth has a unique atmosphere, composed of approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace amounts of other gases, which creates the conditions necessary for life to thrive.
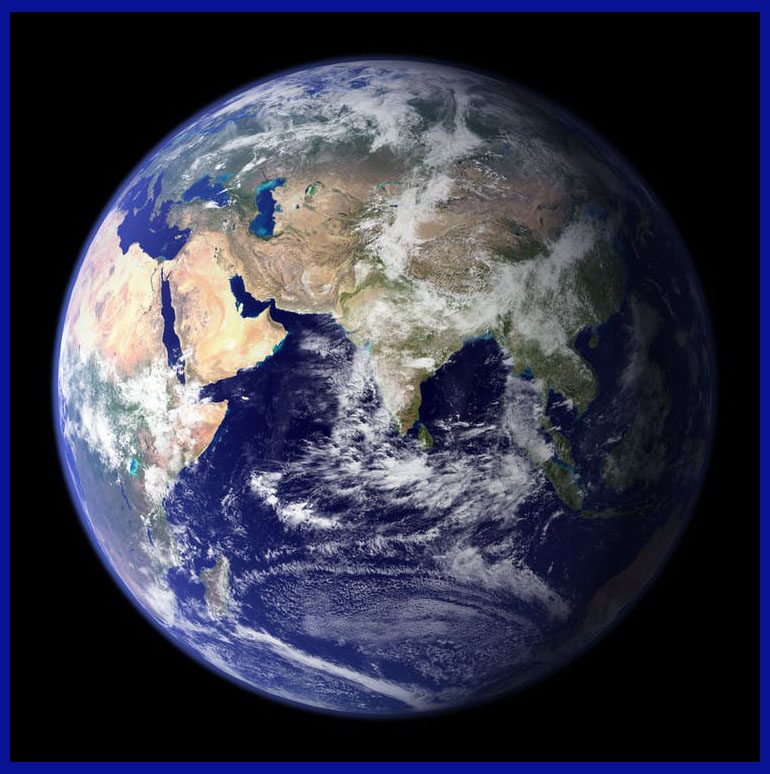

The planet is also characterized by its abundant water, with oceans covering over 71% of the surface. Earth has a single, relatively large moon and is the only planet known to have active plate tectonics, which creates earthquakes and volcanic activity. It also has a magnetic field that protects the planet from harmful solar winds. Humans have inhabited Earth for thousands of years and have made significant advances in technology, science, and exploration of the planet and beyond.
The Planet Mars: Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It has rocky and clay rich in iron, which gives it a red colour. Therefore, it is also called the Red Planet. Mars also has some of the tallest volcanoes and deepest valleys in the solar system. It has a diameter of 6,779 kilometres, which is about half the size of Earth, and has a thin atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide. Mars is characterized by its dusty, rocky terrain, and it has the largest volcano, the deepest canyon, and some of the highest mountains in the solar system. Mars is also known for its two small moons, Phobos and Deimos.
The planet has been explored by a number of spacecraft, including NASA’s Mars rovers, which have discovered evidence of ancient water on the planet’s surface, suggesting that Mars may have once had conditions favourable for the development of life. Mars remains a focus of exploration and study, as scientists continue to investigate the potential for past or present microbial life on the planet.
A Few facts _
- The temperature on the surface of Venus can reach about 465 degrees Celcius
- Earth rotates on its axis and takes 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4.09 seconds to complete one orbit.
- Mars has clouds in its atmosphere and ice at its north pole

What Do You Know About Outer Planets?
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are the outer planets of the solar system. They are larger than the inner planets. The outer planets are gaseous giants with rings around them. The space between the inner and outer planets is filled with rocky material and is known as the asteroid belt.
They have thick atmospheres with no solid surfaces, and they are known for their distinctive and colourful cloud bands and storms.
Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system and has a strong magnetic field, while Saturn is known for its prominent ring system. Uranus and Neptune are characterized by their icy atmospheres and their unusually tilted axes of rotation.
The outer planets also have numerous moons, some of which are quite large and complex, and they have been the subject of extensive study by space probes such as NASA’s Voyager and Cassini missions. Despite their remote location, these planets play an important role in the dynamics of the solar system, influencing the orbits of other planets and objects through their gravitational forces.

The Planet Jupiter: Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system. It is a huge ball of gases and liquids with a small solid centre or core. The planet is topped by dense red, brown, yellow and white clouds. These clouds change their colour daily.
It has a diameter of over 86,000 miles and is fifth from the sun. It is a gas giant, composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, with a strong magnetic field and many moons. Jupiter’s iconic Great Red Spot is a storm larger than the size of Earth and has been raging for over 300 years. Studying Jupiter provides valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system.
The Planet Saturn: Saturn is the second largest planet. It is surrounded by a flat layer of thin rings. The layer has seven broad rings with thousands of narrow ringlets. These ringlets are made of billions of pieces of dust and ice. These pieces could be as small as pebbles or as large as skyscrapers.
Saturn’s atmosphere is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, and it has many moons, with the largest being Titan. The planet’s distinctive hexagonal cloud pattern at its north pole is also a notable feature. The study of Saturn and its rings has provided important insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system and continues to fascinate scientists and astronomers alike.
The Planet Uranus: Uranus is the seventh planet in the solar system. It is covered by bluish-green clouds. These clouds are made of methane gas. Uranus also has eleven rings made of dark rock-sized particles.
It is known as an “ice giant” due to its composition of water, methane, and ammonia ice, which make up a significant portion of its mass. Uranus has a unique feature, with its axis tilted at an extreme angle of almost 98 degrees, causing its seasons to last for over 20 years each. The planet has a faint set of rings and a system of 27 moons, with the largest being Titania and Oberon. The study of Uranus has revealed important information about the formation and evolution of the solar system and continues to fascinate astronomers and researchers.
The Planet Neptune: Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the sun. It is so far that it cannot be seen without a telescope. The surface of Neptune has large dark circles that could be storms. Fast winds blow on the planet all the time. They can reach a speed of 2,000 km/ph.
It is located in the outermost region of our solar system. It is also known as an “ice giant” due to its composition of water, ammonia, and methane ice, which gives it its distinctive blue colour. Neptune has the strongest winds in the solar system, with gusts reaching up to 1,200 miles per hour. The planet has a system of 14 known moons, with the largest being Triton. It also has faint rings, which were discovered in 1984. The study of Neptune has provided valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system and continues to be an area of interest for astronomers and researchers.
A Few Facts _
- The great Red Spot on Jupiter is a hurricane-like storm in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Saturn takes 29.5 Earth years to go around the Sun.
- Neptune takes 165 Earth years to go around the Sun
How Many Moons Are In Our Solar System?
Moons are natural satellites of planets. Natural satellites are objects that orbit around planets. Moons are smaller than the planets around which they orbit.
There are 214 confirmed moons in our solar system, orbiting around eight planets, several dwarf planets, and some large asteroids. The largest number of moons in our solar system belongs to the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn, with 79 and 82 confirmed moons respectively.
Uranus has 27 confirmed moons, and Neptune has 14 confirmed moons. Even Mars has two small moons called Phobos and Deimos, and Earth has one large natural satellite, the Moon. Some of these moons have fascinating features and environments, which make them intriguing targets for exploration and study.
Saturn’s Moons: Saturn has 25 moons that measure at least 9 km in diameter. Titan is Saturn’s largest moon and it is one of the few satellites in the solar system that has an atmosphere similar to Earth’s.
Mars’ moons: Mars is our nearest neighbour in the solar system and has two moons– Phobos and Deimos. They are not spherical like most moons but are uneven and look more like potatoes.
Earth’s Moon: Earth has only one moon. The Moon has plains, mountains and valleys. However, there is no air on the moon so humans cannot live there. The moon rotates on its axis once every 29.5 days and completes one orbit of the earth every 27.3 days.
Jupiter’s Moons: Jupiter has the highest number of moons of all the planets. It has 63 moons, four of which are the largest in the solar system. The four largest moons are- Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto.
A Few Facts _
- A total of 12 astronauts have walked on the moon
- Many of the moons of Uranus are named after the characters of Shakespeare’s plays.
- On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first person to land on the Earth’s moon.

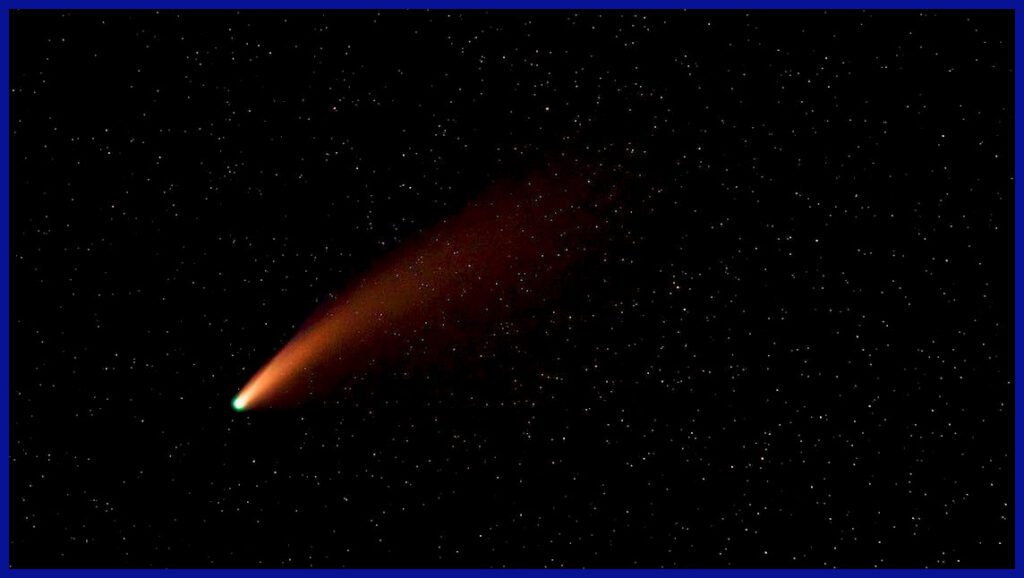
What Do You Know About A Comet In Space?
Comets are small icy bodies that orbit around the Sun. Comets are icy remains of Rocks, gases and dust. Most comets cannot be seen with the naked eye. Some comets, however, become visible as they pass close to the Sun. Comets make a streak of bright light as they pass close to the Sun.
Parts Of A Comet: The head of a comet is a solid core made of icy dust and rock particles. It is surrounded by a cloudy atmosphere known as the coma and has one or two tails. The dust and gas of the coma and the tails reflect Sunlight, which allows us to see the comet from Earth.
Birth Of Comets: Astronomers believe that most of the comets come from two regions – the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud. The Kuiper belt is a space of icy remains between Neptune and Pluto. The Oort Cloud is a circular covering that surrounds the solar system.
Occasionally, due to gravitational disturbances or collisions, comets are sent hurtling towards the inner Solar System. As comets approach the Sun, they heat up and release gas and dust, creating a glowing head (coma) and a tail that can be seen from Earth. The release of gas and dust is what creates the characteristic “tail” that is visible from Earth.
Overall, the birth of comets is believed to be closely linked to the formation and evolution of our solar system, and their study continues to provide valuable insights into the early history of our celestial neighbourhood.
Types Of Comets: Comets can be short-period comets or long-period comets. Their type is determined by how much time they take to complete an orbit around the Sun. Short-period comets come from the Kuiper Belt and they take less than 200 years to complete one orbit. Long-period comets come from the Oort Cloud and they take more than 200 years to complete one orbit.

Understanding the Difference Between Asteroids and Meteors
Asteroids are small rocky bodies that move around the Sun. Asteroids can be as small as a pebble or as large as a few hundred miles in diameter. Meteors are bright streaks of light falling on Earth. They appear when metal or stony matter burns up when entering the earth’s atmosphere.
A meteor, also known as a shooting star, is a streak of light that occurs when a small rocky or metallic object, such as a meteoroid or asteroid, enters the Earth’s atmosphere and burns up due to friction. The object itself is called a meteoroid, and if it reaches the ground without completely burning up, it is called a meteorite. In summary, asteroids are larger objects that orbit the Sun, while meteors are smaller objects that enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up, causing a streak of light in the sky.
Difference Between An Asteroid And A Comet: Asteroids are different from comets only in their composition. Asteroids are made up of metals and rocky materials while Comets are made up of Ice, dust and rocky materials. Asteroids were formed as a result of cosmic explosions which happened about 4.5 billion years ago.
About Meteoroids And Meteors: Mateoroids are boulder-sized debris of metallic or stony matter that travel around the Sun in orbit. When meteoroids enter the Earth’s atmosphere, they burn up because of friction with Earth’s atmosphere. This creates streaks of light in the sky, which is why people often call them shooting stars or falling stars. Meteors that reach the Earth’s surface are known as meteoroids.
A Few facts _
- Every 50 to 100 million years, the Earth is hit by a 10-kilometre-large asteroid
- The largest asteroid created is in Vredefort, South Africa. It is 300 Km in diameter
- Asteroids can also have their own moons

In conclusion, exploring our Sun and all the planets in our solar system is a fascinating and important endeavour. By studying these celestial bodies, we can learn more about the origins and evolution of our solar system, as well as the conditions necessary for the emergence of life. Moreover, exploration of our Sun and planets helps us to better understand the challenges and opportunities for human exploration and settlement beyond our own planet. As we continue to learn more about our Sun and planets through scientific exploration, we can expand our knowledge and appreciation of the wonders of the universe.

Furthermore, an essential piece of information demands attention beyond the scope of this article. Do not overlook the opportunity to seize an exclusive chance to own your very own collection of awe-inspiring, extra-large 1/125 resin scale premium models featuring the British Airways Concorde. These exceptional aircraft, available exclusively through Air Models with worldwide delivery, embody sheer excellence and have gained renown for their unparalleled significance in the realm of the world’s first supersonic passenger plane. Act now to secure your piece before the limited stock is depleted.
Important Announcement for Our Valued Readers!
After an article is published, it is possible that updates or changes may have occurred beyond the time of publication. Therefore, it is important to be aware that certain information in the article might be outdated. To ensure the most accurate analysis, it is highly recommended to verify the content with the latest sources available.
However, we are dedicated to delivering outstanding articles on military products and global updates. Maintaining quality and smooth operation requires resources. Your support sustains our efforts in providing insightful content. By purchasing high-quality products through our affiliated links, you help us keep our platform alive and acquire top-notch items. Your unwavering support is invaluable and inspires us to strive further.
We welcome your suggestions and requests for more information, as we value feedback from our readers. If there’s specific defence material or equipment not covered on our site, please share your request in the comments. We’ll strive to research and provide the required information. We sincerely thank you for your unwavering interest in our website, and we eagerly anticipate hearing from you! Enjoy your reading experience!