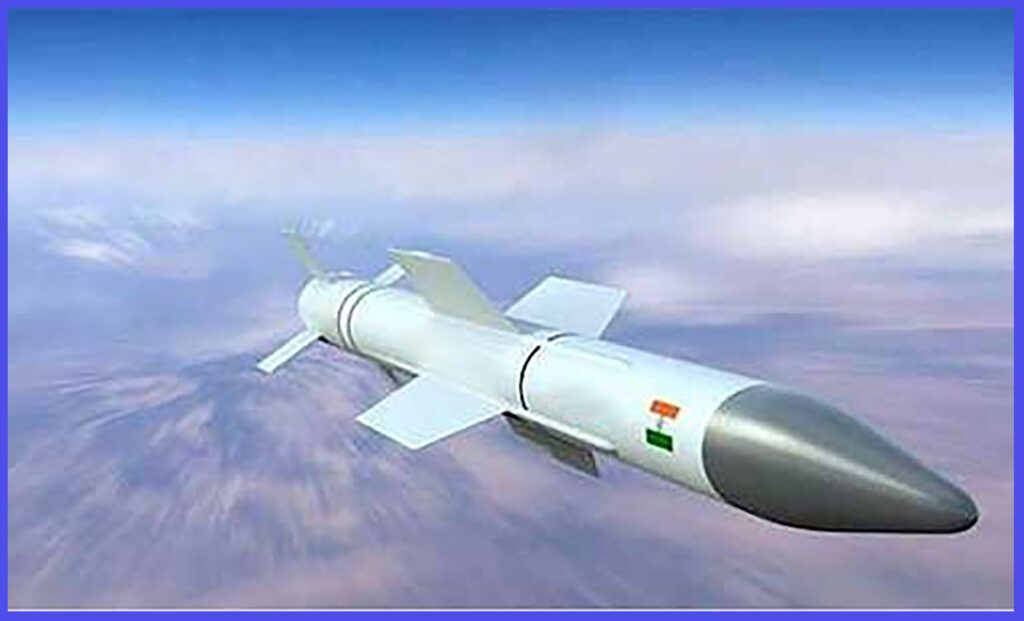
This FOX-3-Type missile is engineered to annihilate any incoming aerial target, regardless of weather conditions. Its sheer power and precision are nothing short of awe-inspiring.
In the air-to-air combat scenario, the ASTRA Missile’s advanced active guidance section and mature seeker design equip it with the ability to detect and track targets in the most hostile environments rapidly. This unique feature empowers the missile to engage and neutralize its target at extended ranges and higher altitudes compared to other similar weapons. In essence, the Missile’s exceptional technology and performance capabilities make it a formidable and reliable air-to-air weapon system.
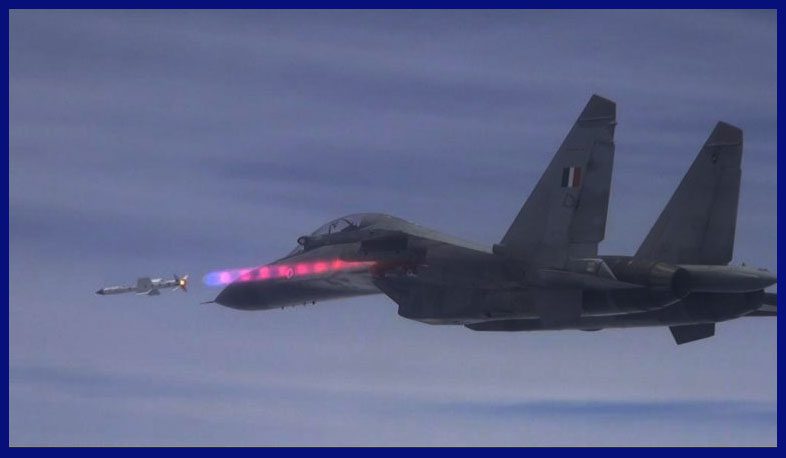

The ASTRA missile is offered in various variants, including the ASTRA Mk-1, which features a range exceeding 110 km, the upgraded ASTRA Mk-2, boasting an extended range of over 160 km, and the ASTRA Mk-3, equipped with an extended range of 350 km for air-to-air kill capability. Both the Mk-2 and Mk-3 variants are currently undergoing rigorous trial phases. Furthermore, a shorter-range version known as Astra IR, with a range of 80 km, is currently in the design and trial phase. For the Indian Navy, the VL-SRSAM has been in active service since 2022.
The missile can engage targets at various distances, ranging from 500 m to a maximum of 350 km. ASTRA Mk-1 has been integrated with the Indian Air Force’s Sukhoi Su-30MKI, MiG-29UPG, and LCA Tejas, as well as the Navy’s MiG-29K. All the variants are expected to be integrated with the Dassault Rafale, the future AMCA, and the TEDBF. Currently, Astra Mk-1 missiles have been in limited series production since 2017.
It employs active radar homing for terminal guiding and mid-course inertial navigation powered by a fibre-optic gyroscope. Using a secure data link, it is able to get course adjustments. The active radar seeker for the missile, with a homing range of 25 km, was created by the Russian company Concern Morinformsystem-Agat but was made in India. The seeker allows off-boresight launches up to a 45° angle and can lock on to a target with a radar cross-section of 5 square metres from a distance of 15 kilometres away.
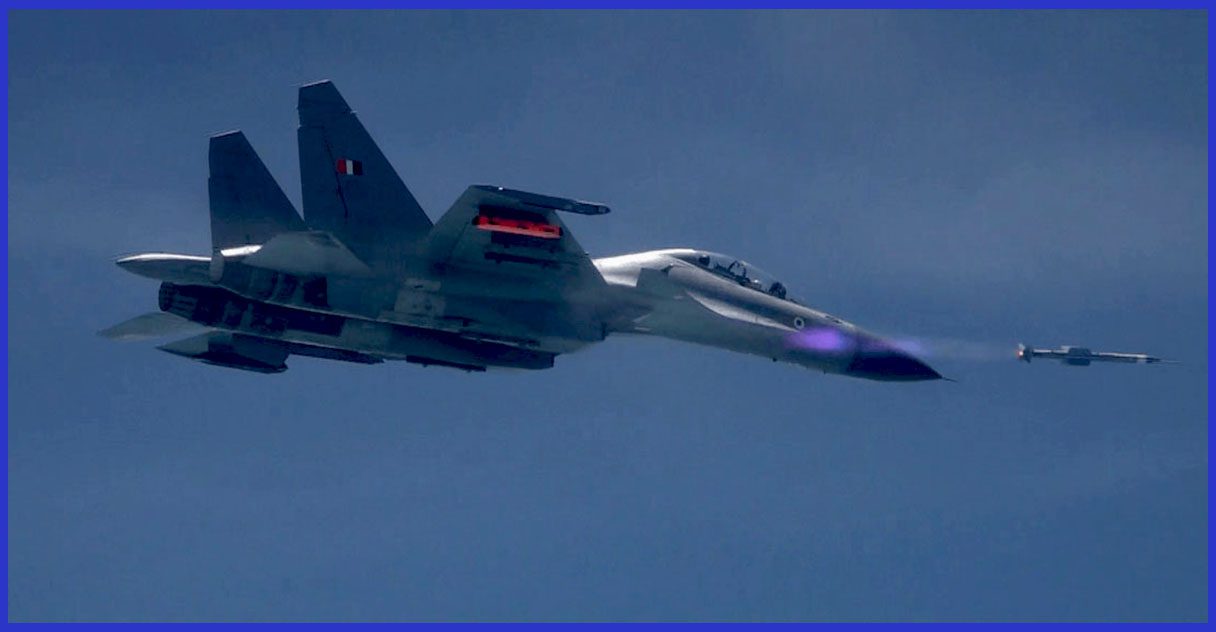

In order to continue operating even when the adversary tries to jam the seeker with electronic countermeasures, the original Astra Mk-1 is outfitted with electronic counter-countermeasures. It is equipped with a proximity fuse-activated, pre-fragmented explosive warhead weighing 15 kg (33 lb). Operating at a maximum height of 20 km (66,000 ft), the missile can reach a speed of Mach 4.5 thanks to its smokeless solid-fueled motor.
When in tail chase mode, its maximum range is 20 km (12 mi), and when in head-on chase mode, it is 110 km (68 mi). The missile reaches its maximum range when it is launched from a height of 15 km (49,000 ft). Its range decreases to 44 km (27 mi) when shot from an altitude of 8 km (26,000 ft), and to 21 km (13 mi) when launched from sea level.
Astra can engage manoeuvring targets up to a distance of 90 km (56 mi) in head-on pursuit mode and 60 km (37 mi) in tail chase mode thanks to its low aspect ratio wings. It can lock on to its target before or after launch and can operate in both buddy and autonomous modes.
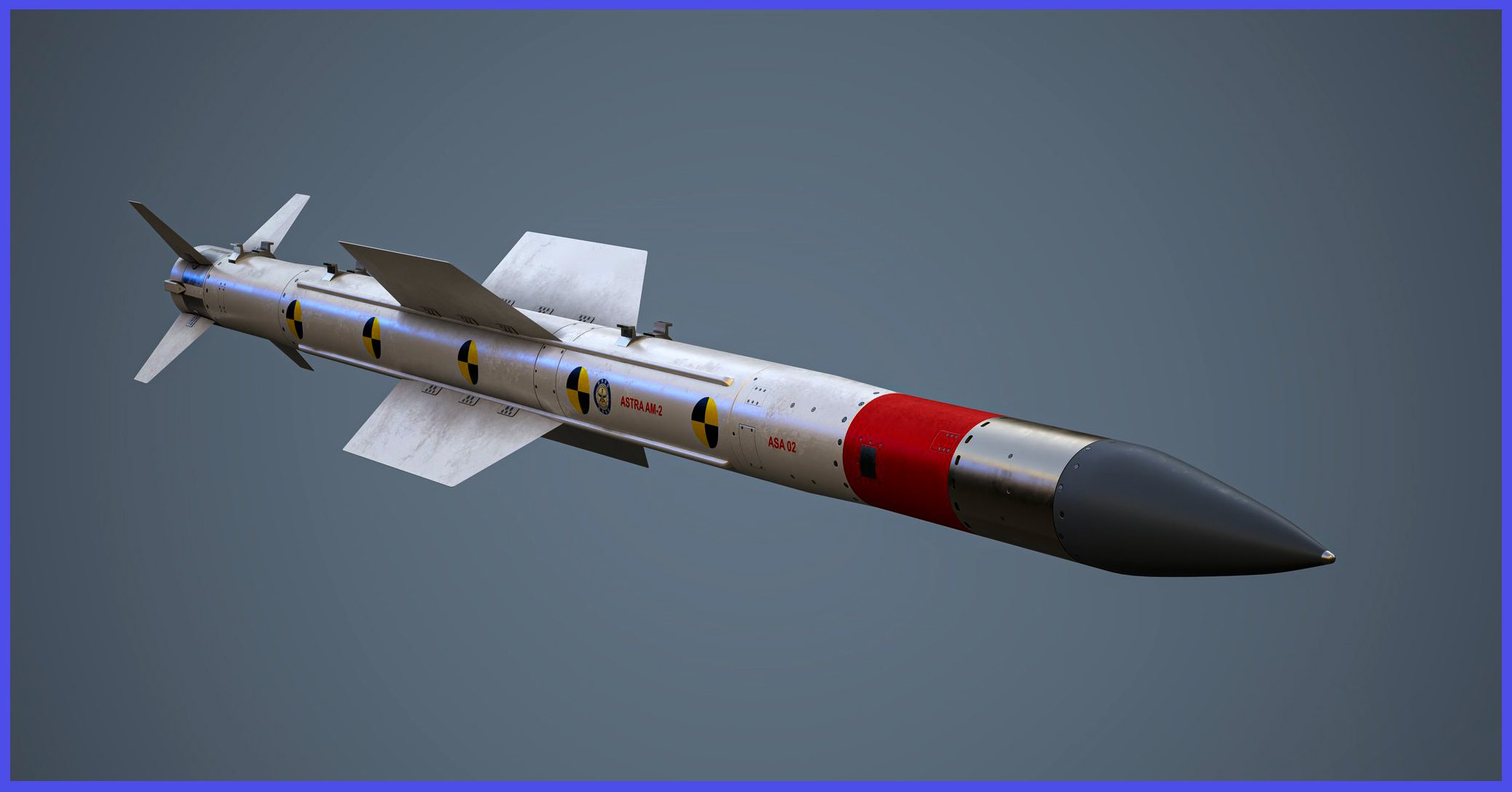


ASTRA Missile Testing and Development
The ASTRA Missile project was initiated by DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation) in the early 1990s, led by the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL) with support from Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and Electronics Corporation of India Limited (ECIL). After the completion of a pre-feasibility study, the official sanction for the missile’s development came in 2004, with a budget of ₹955 crore. The missile underwent a series of developmental tests before receiving clearance for induction into the Indian Air Force (IAF). Over 20 successful flight tests, including live firings from fighter aircraft, have been conducted, demonstrating a high degree of accuracy and reliability.


Following the conclusion of the final round of development trials in September 2017, Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) granted approval for the production of the Astra missile. The initial production is slated to take place in Bhanur, Telangana, starting with a batch of fifty missiles. A further order for 240+ missiles has been placed for use by the Indian Navy and Air Force, to be deployed on a range of platforms, including the Sukhoi Su-30MKI, HAL Tejas, and MiG-29/MiG-29K, among others.
In the high-priority Indian Designed, Developed, and Manufactured (IDDM) category, the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and BDL entered into an agreement on May 31, 2022, for the production of more than 350 Astra Mk-1 units for the Indian Air Force and Indian Navy. The contract carries a value of ₹2,971 crore (US$383 million). The process of transferring missile and related system technology to BDL has already commenced, as per DRDO. Each missile is priced at ₹7-8 crore. It is envisioned that all long-range air-to-air missiles of Russian origin within the Indian Navy will eventually be replaced by Astra Mk-1 and other variants.
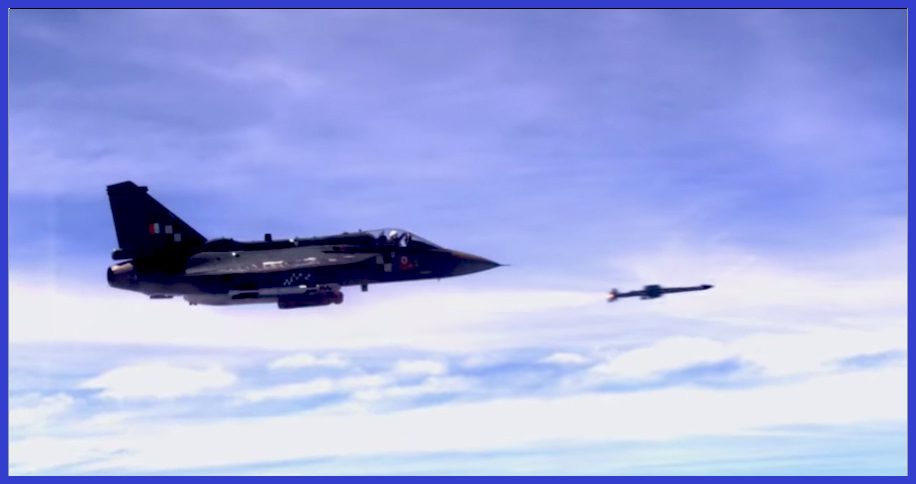


Technology and Features of ASTRA-BVR
The ASTRA Mk-1 incorporates electronic counter-countermeasures to ensure its continued functionality in the face of an opponent’s attempt to jam the seeker using electronic countermeasures. Additionally, it is equipped with a 15 kg (33 lb) pre-fragmented high explosive warhead that is detonated by a proximity fuse. The missile is propelled by a smokeless solid-fueled engine, enabling it to achieve a maximum altitude of 20 km (66,000 ft) and accelerate to a speed of Mach 4.5.
ASTRA can effectively engage manoeuvring targets at distances of up to 90 km in head-on chase mode and 60 km in tail chase mode, a performance attribute attributed to its low aspect ratio wings. The missile has the capability to establish contact with its target either before or after launch, offering the versatility of being launched in either an autonomous or buddy mode of operation.


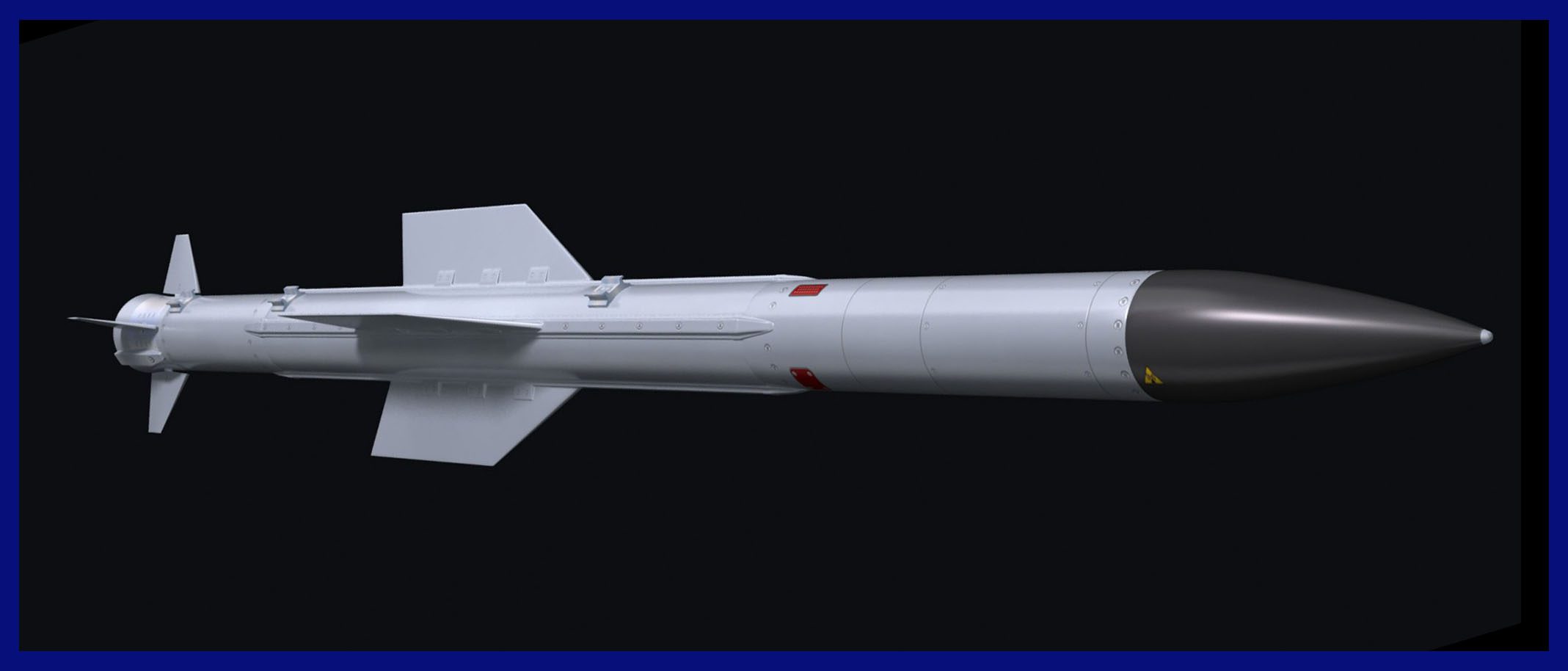
Near Future Programme: With the deployment of Astra Mk-1, a number of offshoot variants are being considered, including an image Infra-red homing missile that is now known as ASTRA-IR, a more advanced ASTRA Mk-2 version, and ASTRA Mk-3.
A dual-pulse rocket motor, developed in-house by India’s DRDO, will be employed to enhance the range of the ASTRA missile’s Mark 2 variant by July 2022. The missile will feature a laser proximity fuze, incorporate newer technologies such as a domestic AESA radar seeker, maintain a design similar to its predecessor, the Mk-1, and utilize smokeless propulsion. DRDO aims to increase the Mk-2 version’s range to 160 kilometers.


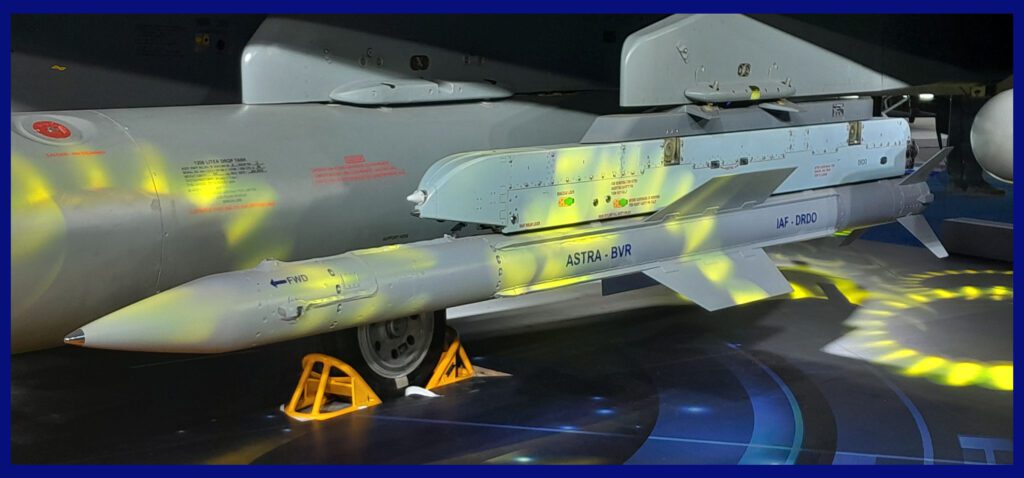
Future Development Version Of ASTRA-BVR
India and Russia are working together to build a future Mk-3 model powered by a solid fuel ducted ramjet ( SFDR ) engine. The missile had two tests, one on May 30, 2018, and the other one on February 8, 2019. The program’s goal is to create a homegrown missile that can compete with the MBDA Meteor and AIM-260 JATM. An upgraded version of the missile will have a range of over 300 km. The ASTRA Mk-3 is expected to be a game-changer in India’s air defence strategy, and its development is being closely watched by the global defence industry.
Export Potential Of ASTRA BVR
Several nations have expressed interest in the ASTRA Missile, including Malaysia, Vietnam, and Indonesia. The missile has been on display at a number of international defence shows, and the DRDO is aggressively seeking export options for it. It was reported in August 2023 that, as a more affordable alternative, Brazil was looking into the prospect of fitting its Gripen aircraft with Astra Mk1 missiles.


Salient Features Will Be:
- ASTRA is a BVR class missile with a proven flight range of 85+ km.
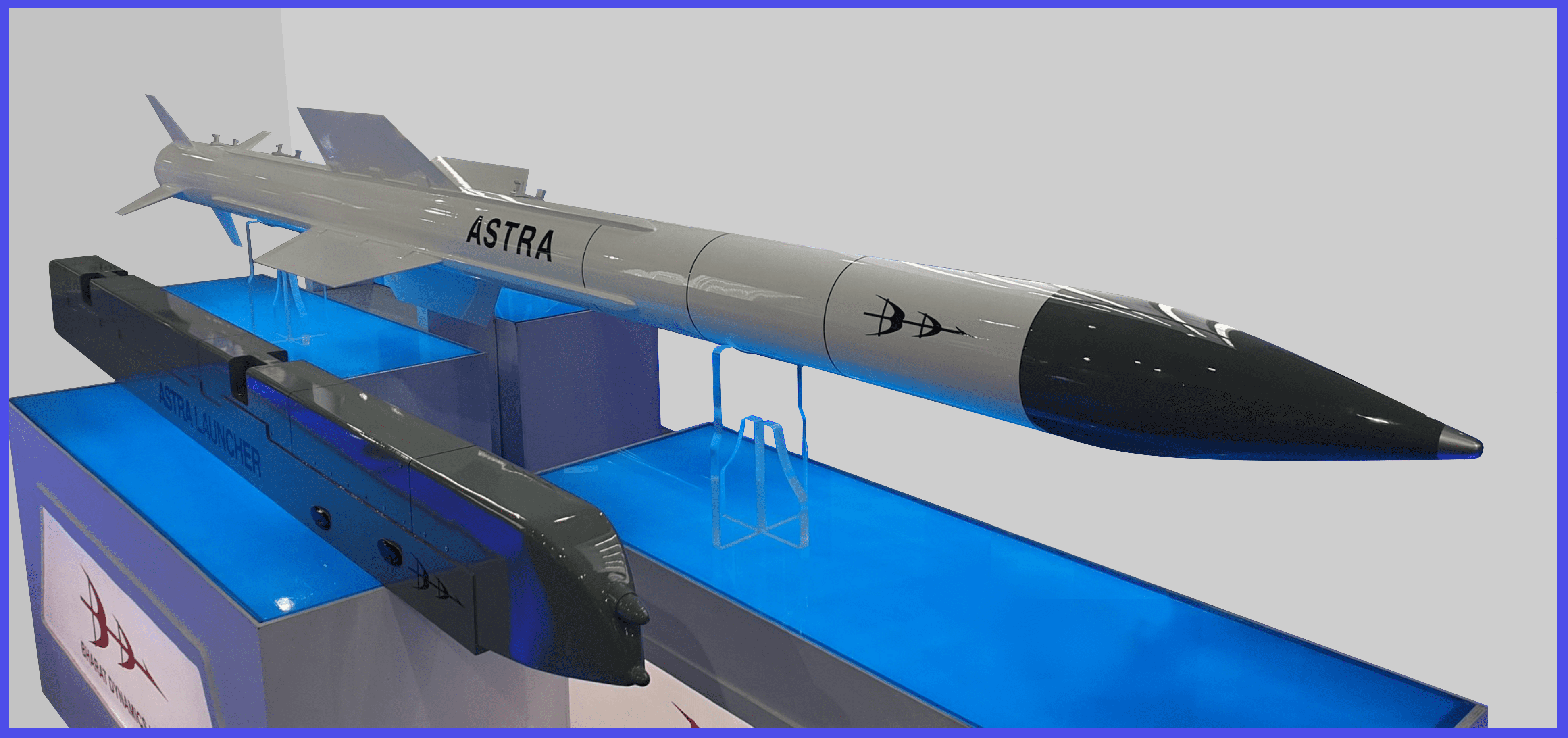
- The missile is configured with a diameter of 178 mm and a length of 12.6 ft. Its launch mass is 170 kg.
- The missile can be fired using a rail type of launcher
- It is equipped with a Mid-course inertial guidance system followed by terminal homing guidance.
- The mid-course guidance is carried out on the basis of target updates received via data link.
- The RF seeker provides a large autonomous range for the terminal phase.
- The missile is equipped with a highly accurate proximity fuse and fragmented type warhead to ensure a high kill probability
- Integration of ASTRA missiles with the primary fighters of the IAF has been carried out successfully.
- The missile system is platform-independent and it can be integrated with other aircraft.


ASTRA Air-to-Air Missile Specifications
- Weight: 154 kg ( 340 lb )
- Length: 12.6 ft ( 3.84 m )
- Diameter: 7 in ( 178 mm )
- Warhead: High Explosive Pre-fragmented, weighing 15 kg ( 33 lb )
- Detonation: Mk-1 has a Radio proximity fuse and Mk-2 Optical proximity fuze
- Engine: Solid propellant rocket
- Range: Astra Mk-1: 110 km (68 mi) / Astra Mk-2: 160 km (99 mi) / Astra Mk-3: 350 km (220 mi) and Astra IR: 80 km (50 mi)
- Service Ceiling: around 66,000 ft
- Speed: Mach 4.5
- Guidance: Inertial Navigation System ( INS ) with mid-course update via data link and active radar homing
- Launch Platform: SU-30MKI, MiG-29UPG, MiG-29K, Tejas, and work in progress for integration into Dassault Rafale, as well as for future projects such as AMCA and TEDBF aircraft
The Surface-to-Air (SAM) Version Is Also Progressing in Parallel with VL-SRSAM


The VL-SRSAM (Vertical Launch-Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile)
Is an advanced missile system specifically engineered to provide short-range air defence capabilities for naval vessels. This system, developed by India’s Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), demonstrates exceptional versatility and the capability to effectively engage a broad spectrum of aerial threats, encompassing incoming missiles, hostile aircraft, helicopters, and high-speed drones.
What sets the VL-SRSAM apart is its vertical launch capability, which allows for 360-degree coverage and rapid reaction times. The system is integrated with advanced radar and fire control systems, ensuring precision and reliability in neutralizing airborne threats, making it a valuable asset for maritime security and naval operations.
The missile employs an inertial guidance system relying on a fibre-optic gyroscope during its mid-course flight phase, while it switches to active radar homing during the terminal phase. Mid-course updates are received via datalink, and the missile is equipped with both lock-on-before-launch (LOBL) and lock-on-after-launch (LOAL) capabilities. The VL-SRSAM has been specifically designed to replace the older Barak 1 surface-to-air missile system that was previously deployed on Indian Navy vessels. Additionally, the Indian Air Force is set to deploy it as a short-range air defence system.

To meet the Indian Navy’s demand for replacing the Barak-1 short-range surface-to-air missile system, the DRDO conducted a successful test of two VL-SRSAM (Vertical Launch-Short Range Surface-to-Air Missiles) on February 22, 2021, near the coast of Odisha. The initial launch assessed the missile’s capabilities, including its maximum and minimum range, as well as the effectiveness of the vertical launch system. Both missiles effectively and accurately engaged their intended targets during the test. The missile’s agility is enhanced by thrust vectoring control based on jet vanes.
Much like the Norwegian/American NASAM 2 system, the Indian Air Force is considering the utilization of truck-based launchers for the VL-SRSAM to enhance the Akash surface-to-air missile, creating a rapid-response capability.
The VL-SRSAM Design
The VL-SRSAM is derived from the Astra Mark 1 air-to-air missile, featuring four aerodynamically stable short-span long-chord cruciform wings. It incorporates jet vane-driven thrust vector control to ensure smokeless exhaust and rapid response during vertical launches. The primary purpose of the VL-SRSAM is to provide protection for naval platforms in both area and point-defence roles. Depending on the available space on the ship, a multiple launch system arrangement can be installed for each Vertical Launch System (VLS). This VLS is capable of accommodating up to forty missiles, organized in a twin quad-pack canister configuration, with each canister containing eight missiles for hot launch.
As reported, the missile finds deployment on aircraft carriers, frigates, destroyers, and corvettes. The missile system was conceived and engineered as a component of the Development cum Production Partner program (DCPP), with contributions from the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), Research & Development Establishment (Engineers), Research Centre Imarat (RCI), as well as some private sector enterprises.


Alongside this article, seize the exclusive opportunity to acquire a 1/72 scale premium diecast model of a Sukhoi SU-30SM Russian Knights, a highly agile multirole combat aircraft. These extraordinary and renowned military aircraft, celebrated as the pinnacle of advanced and sophisticated fighter planes, are currently available for purchase through AirModels, with global delivery options. Act promptly to secure these exceptional models before the limited stock is depleted.
In conclusion, the ASTRA missile stands as a testament to India’s prowess in defence technology development. With its cutting-edge design, advanced guidance systems, and versatility, it has become a pivotal asset for the Indian Air Force and Navy, ensuring air superiority and bolstering national security. The successful development and deployment of ASTRA highlight India’s commitment to reducing dependency on foreign defence systems and advancing its indigenous capabilities. This state-of-the-art air-to-air missile not only safeguards the nation’s skies but also underscores the nation’s dedication to innovation and self-reliance in the realm of defence, positioning India as a formidable force on the global stage.



Important Announcement for Our Valued Readers!
After an article is published, it is possible that updates or changes may have occurred beyond the time of publication. Therefore, it is important to be aware that certain information in the article might be outdated. To ensure the most accurate analysis, it is highly recommended to verify the content with the latest sources available.
However, we are dedicated to delivering outstanding articles on military products and global updates. Maintaining quality and smooth operation requires resources. Your support sustains our efforts in providing insightful content. By purchasing high-quality products through our affiliated links, you help us keep our platform alive and acquire top-notch items. Your unwavering support is invaluable and inspires us to strive further.
We welcome your suggestions and requests for more information, as we value feedback from our readers. If there’s specific defence material or equipment not covered on our site, please share your request in the comments. We’ll strive to research and provide the required information. We sincerely thank you for your unwavering interest in our website, and we eagerly anticipate hearing from you! Enjoy your reading experience!

2 thoughts on “ASTRA Air-to-Air Missile”