Its distinctive low-level sea-skimming flight profile enables it to elude enemy radar detection until the very last terminal phase, significantly enhancing its survivability. Fueled by a solid-fuel rocket motor, the missile achieves remarkably high subsonic speeds, reaching up to 620 knots.
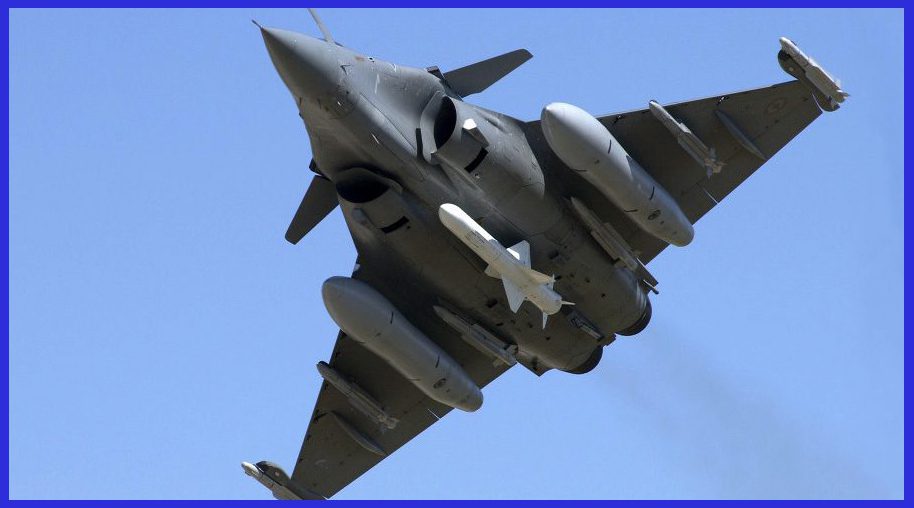

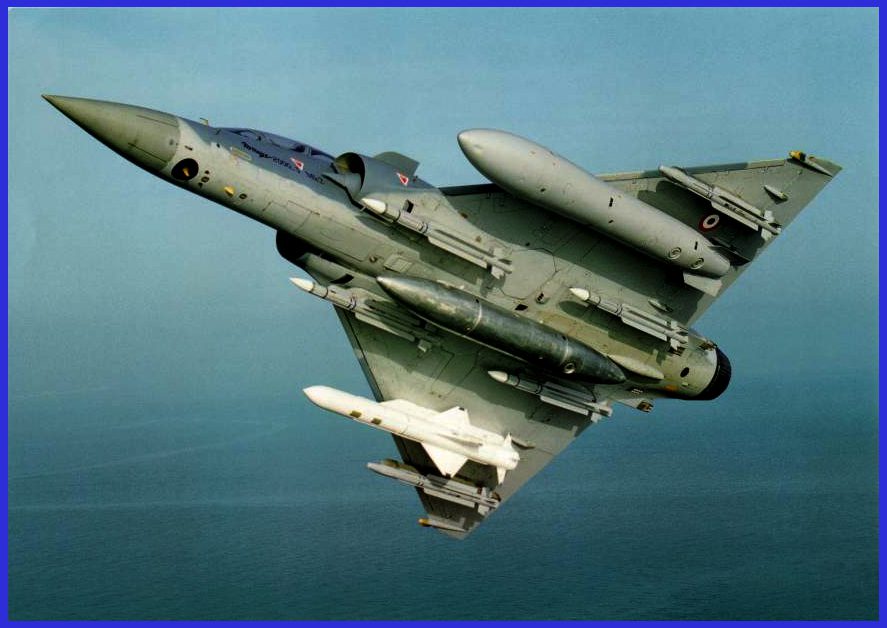
The Exocet can be fired from surface ships, submarines, helicopters, and fixed-wing aircraft in a variety of configurations. Equipped with an active radar-homing seeker, the Exocet autonomously locates and locks onto its target during the final approach, making it a formidable threat against naval vessels. This capability minimizes the need for continuous guidance from the launching platform. The missile carries a warhead designed to inflict significant damage upon impact, ensuring its effectiveness against a variety of naval targets.
Over the years, the Exocet has undergone numerous upgrades, resulting in improved range, accuracy, and countermeasure resistance. Its successful use in various conflicts has solidified its reputation as a reliable and lethal anti-ship missile, contributing to its widespread adoption by naval forces globally.
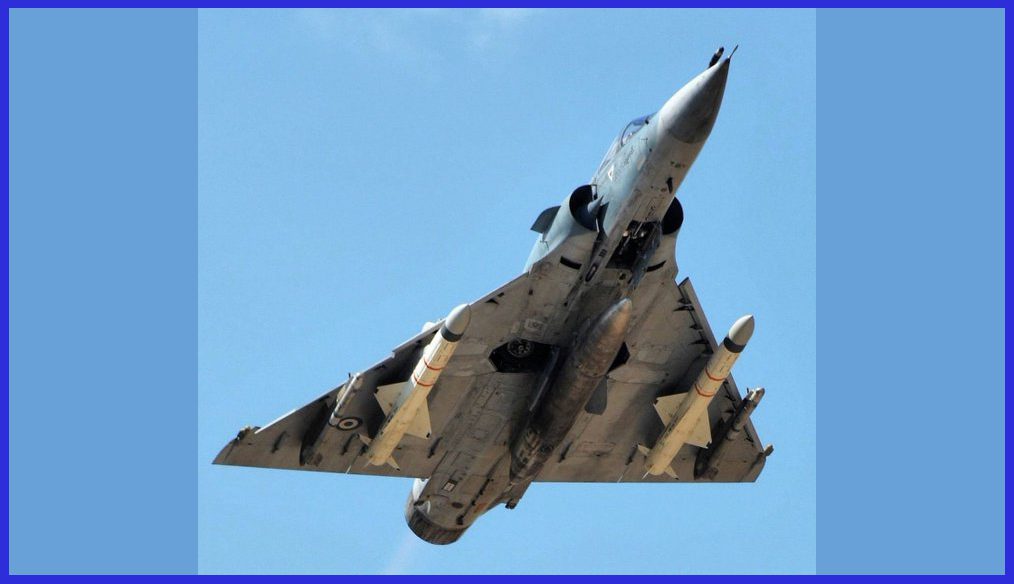

Exocet Missile Background
The Exocet missile is manufactured by MBDA, a prominent European missile company. The developmental journey commenced in 1967 under Nord, initially as a ship-launched weapon known as the MM38. After a few years, Aerospatiale and Nord merged, consolidating their efforts. The foundational body design drew inspiration from the Nord AS-30 air-to-ground tactical missile.
The sea-launched MM38 became operational in 1975, while the air-launched AM39 Exocet started development in 1974, joining the French Navy’s arsenal in 1979. Since 2001, these missiles have been produced by MBDA France. This ongoing collaboration underscores the continual evolution and advancements in Exocet’s production.

The Exocet, a relatively compact missile, is meticulously designed to target small- to medium-sized warships such as frigates, corvettes, and destroyers. Its efficacy extends to larger vessels, including aircraft carriers, where multiple hits can prove effective. Navigated inertially during mid-flight, the missile switches to active radar homing in the late stages to precisely locate and strike its intended target.
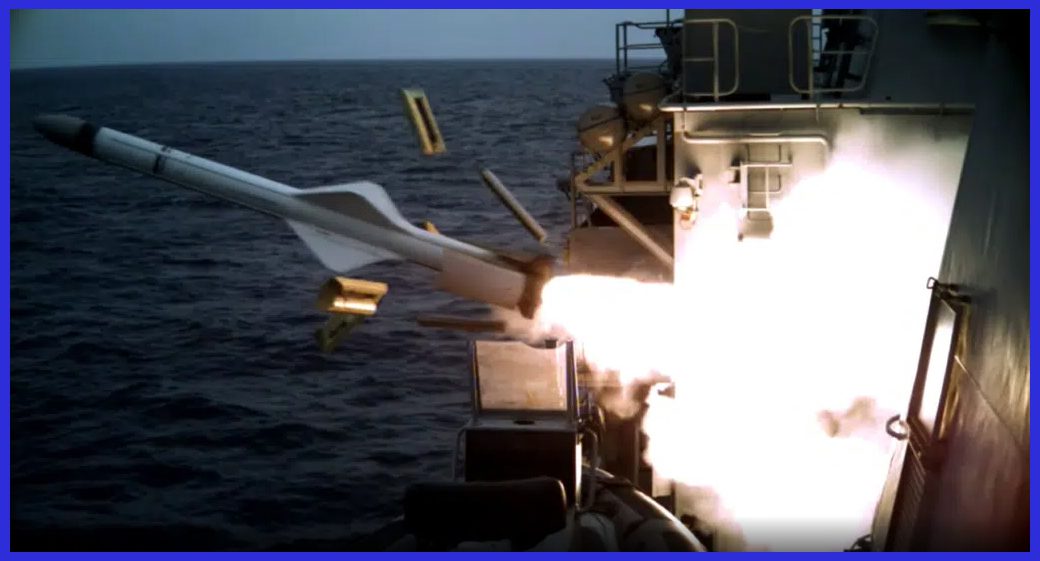
In a strategic countermeasure against air defence systems surrounding the target, the Exocet maintains an exceptionally low altitude during its inbound trajectory, skimming just one to two meters above the sea surface. This deliberate low-altitude approach, coupled with the radar horizon effect, implies that the target may remain unaware of the incoming threat until the missile is merely 6,000 meters (3.7 miles) from impact. This limited reaction time necessitates the development of close-in weapon systems (CIWS) as a crucial defensive measure.

The air-launched Exocet, propelled by a solid propellant rocket motor, showcases an impressive maximum range of 70 kilometres (38 nautical miles). Noteworthy advancements were introduced in the Block 3 MM40 ship-launched version, where the original solid-propellant booster was replaced with a turbojet sustainer engine. This significant modification substantially extends the missile’s operational range to nearly 200 kilometres (110 nautical miles), marking a notable enhancement in its overall capabilities. These innovations in propulsion technology underscore the continuous efforts to refine and expand the Exocet missile’s range, ensuring its effectiveness in diverse operational scenarios.

Variants of the Exocet Anti-Ship Missile
The Exocet missile has evolved over the years, leading to the development of several variants, each with enhancements in range, guidance systems, and countermeasures.
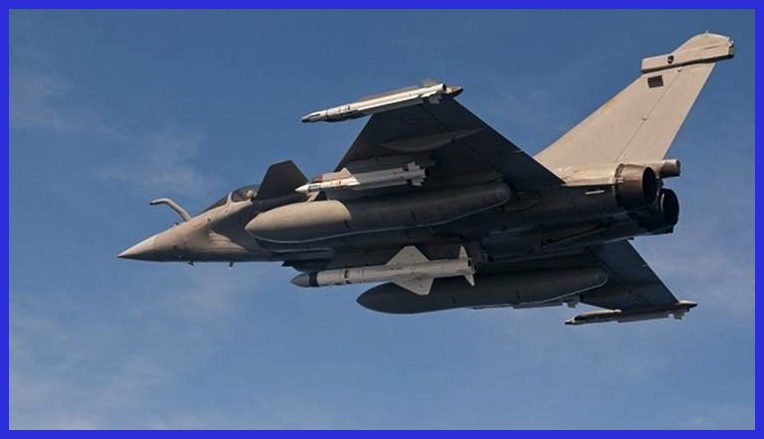
The Exocet AM39, B2 Mod 2: stands as the airborne variant within the Exocet anti-ship missile family. It finds deployment from a variety of aircraft, including Strike Aircraft, Maritime Patrol Aircraft, and Helicopters. Functioning as a Fire-and-Forget missile, this variant has earned its place in active service with the French Navy and an additional 11 nations.

With a range extending up to 70 kilometres, contingent upon the altitude and speed of the launching aircraft, the Exocet AM39 provides a strategic advantage by allowing the aircraft to operate within a safe distance from enemy air defences. Particularly adept at low-altitude attacks, the missile may be launched beneath the radar coverage of the target ship, ensuring a tactical advantage. The unique sea-skimming approach during ingress further enhances the partial stealth and effectiveness of the Exocet AM39 in a variety of operational scenarios.
Exocet AM39 Specifications
- Weight: 670 kg (1,477 lb)
- Length: 4.69 meters (15.38 ft)
- Diameter: 350 mm (35 cm)
- Wingspan: 1.35 m (4 ft 5 in)
- Range: 50 to 70 km (38 nmi)
- Speed: High subsonic, Mach 0.93 / 1,148 km/h (713 mph)
- Guidance system: Inertial guidance, Active radar homing

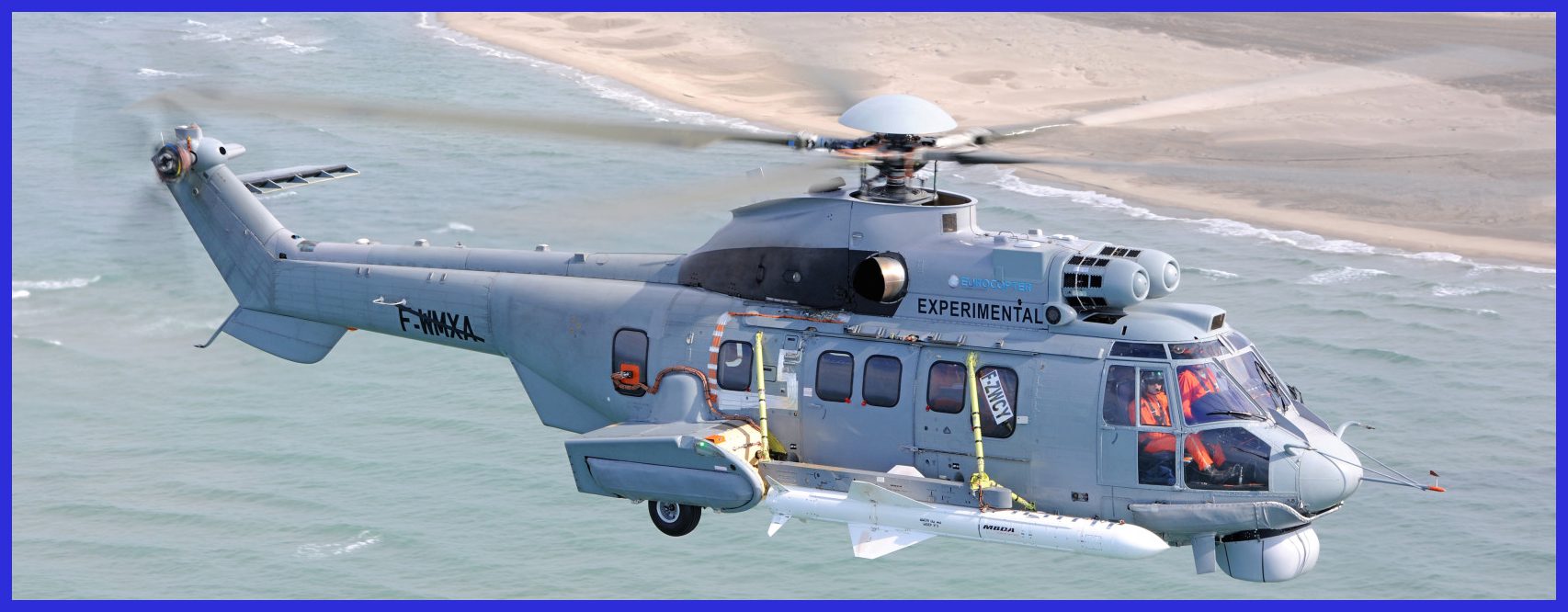
The Exocet SM39, B2 Mod 2: is the submarine-launched version designed for underwater platforms within the Exocet family. It encompasses all-weather capability, sea-skimming flight, a solid-fuel booster for submarine launch, and a high-kill warhead weighing 165 kg (364 lb).
The missile is designed to be housed inside a watertight launched capsule, which can be fired from the submarine’s 21-inch torpedo tubes. Upon leaving the water, the capsule is ejected, and the missile’s motor is ignited. It then rapidly homes in on the target at the sea-skimming level, utilizing an inertial navigation system followed by autonomous terminal guidance from an active RF seeker. Subsequently, it behaves like an MM40 surface-launched version. The system is designed to be fired at depth, making it particularly suitable for discreet submarine operations.
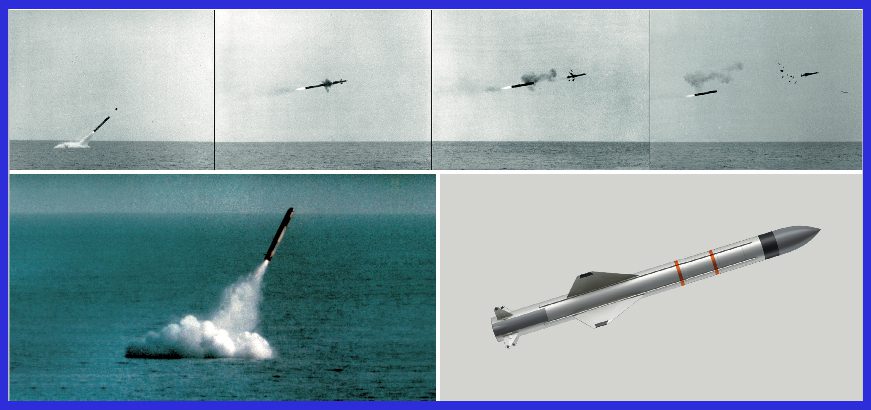
The missile boasts a range of 50 km (27 nautical miles), allowing the submarine to engage in action while staying beyond the reach of enemy detection and weapon range. The system’s flexibility and versatility are enhanced through its large launch envelope.
Exocet SM39 Specifications
- Weight: 655 kg (1,444 lb)
- Length: 4.69 meters (15.38 ft)
- Diameter: 350 mm (35 cm)
- Wingspan: 1.35 m (4 ft 5 in)
- Range: 50 km (27 nmi)
- Speed: High subsonic, Mach 0.93 / 1,148 km/h (713 mph)
- Guidance system: Inertial guidance, Active radar homing
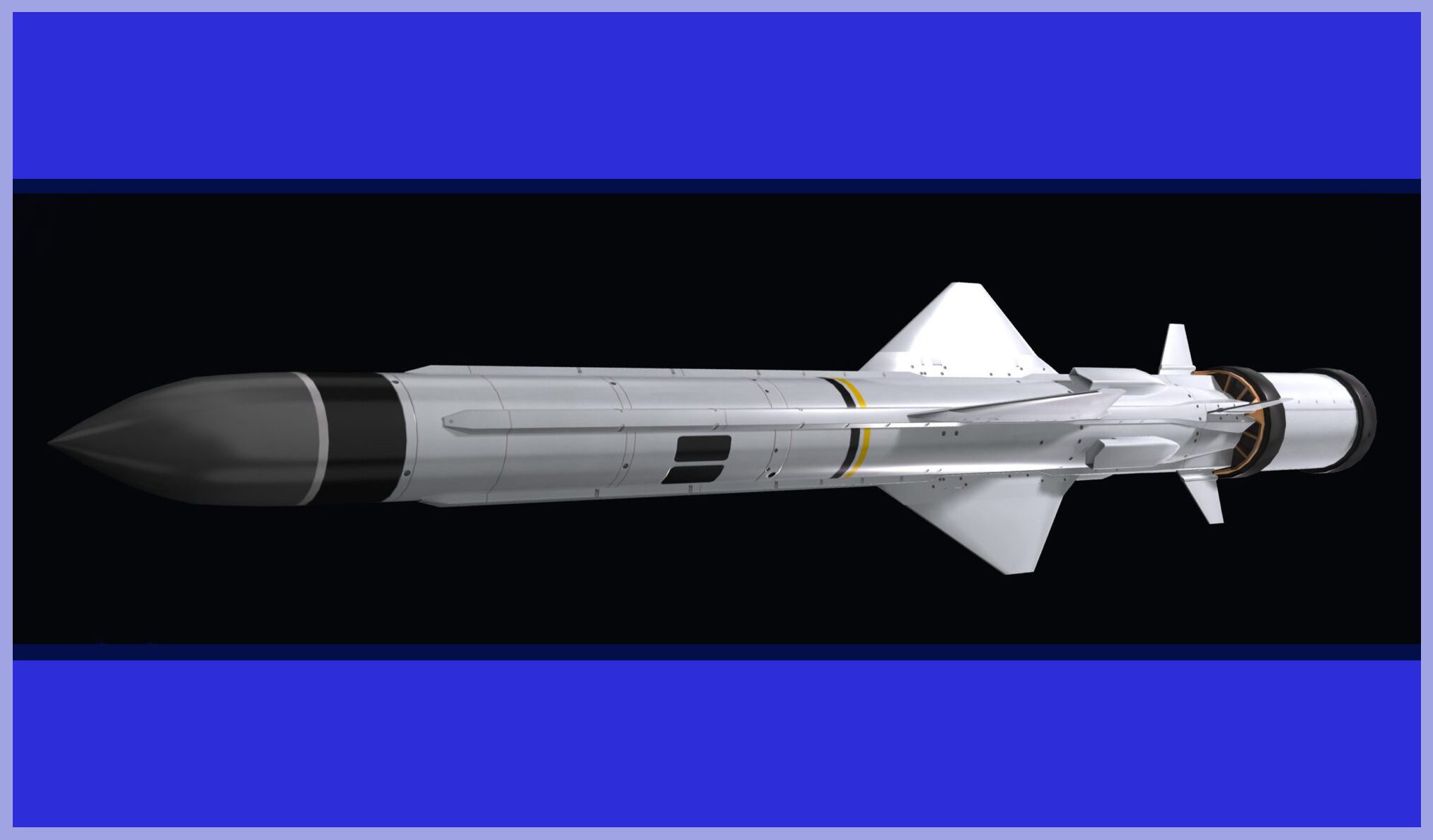

The Exocet MM40: a surface-launched version, has various iterations including Block 1, Block 2, and Block 3, which are deployed on warships and in coastal batteries. The range is 72 km for Block 2 and over 200 km for Block 3.
The MM40 Block 3 is the latest generation ship-borne version within the Exocet family, currently in operational service with several navies globally. This advanced system offers improved operational performance and incorporates technology upgrades, all while minimizing the impact on procurement and logistic support costs. The MM40 Block 3 includes a Mission Planning software module that automatically computes engagement plans to support firing decisions.
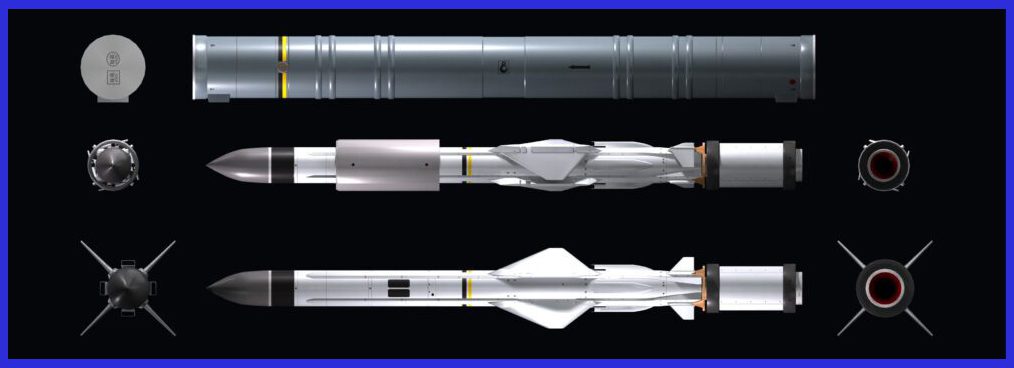
The versatility of the MM40 Block 3 weapon is augmented by the precision of the new navigation package, enabling optimized 3D approach trajectories and terminal attacks from various azimuths, at extremely low sea-skimming altitudes, with simultaneous time on target. The terminal guidance relies on a sophisticated J-band active seeker for discriminating and selecting sea targets, while GPS accuracy is utilized for land targets.
The MM40 Block 3 is designed to seamlessly integrate with the majority of existing logistic support assets in service. Its launching system is fully interoperable with all MM40 versions, ensuring a smooth and efficient transition to Block 3. According to MBDA, the BLOCK 3 shipset exhibits versatility, allowing for installation on a diverse range of naval platforms.

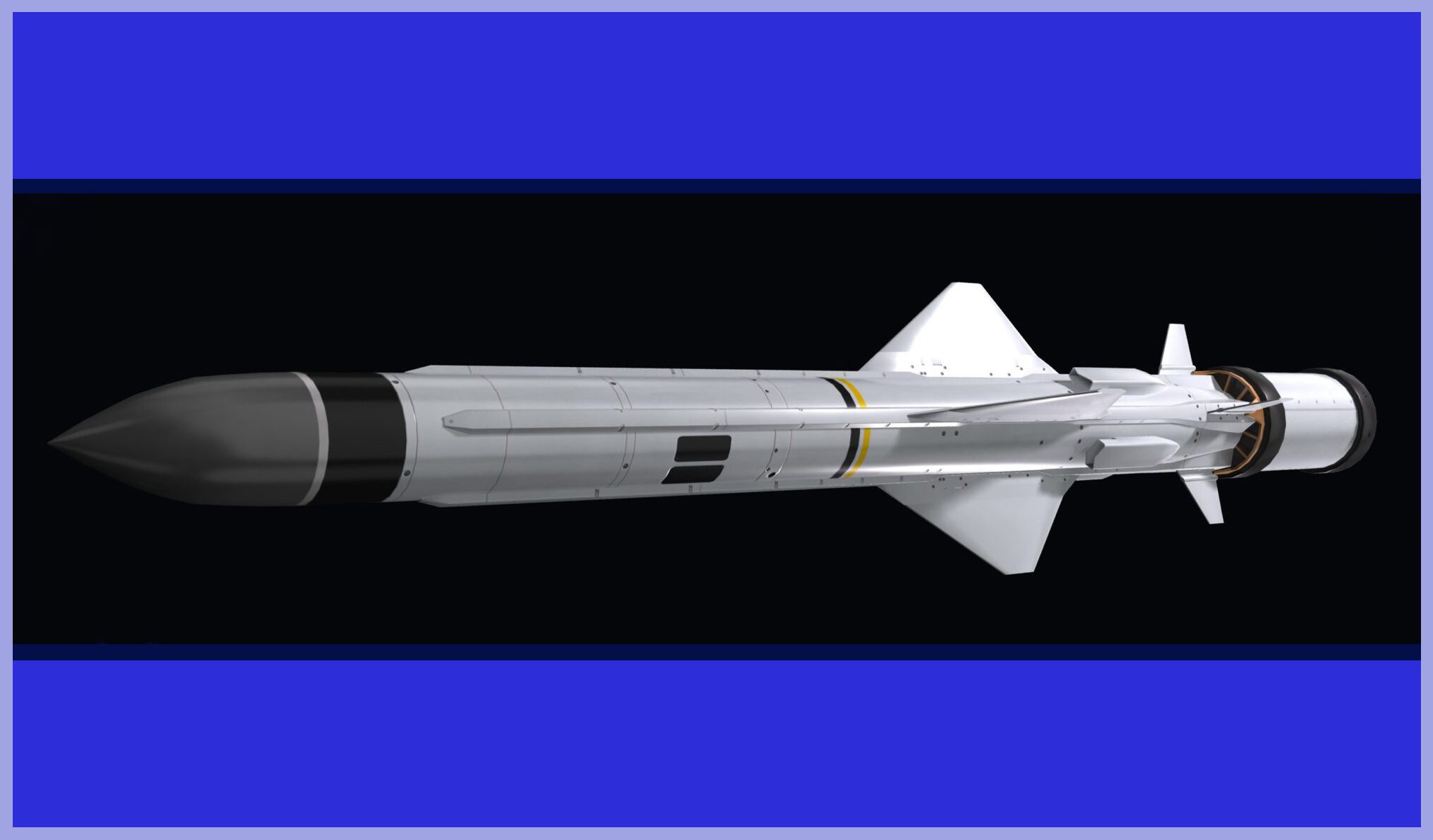
Exocet MM40 Block 3 Specifications
- Weight: 780 kg (1,720 lb)
- Length: 6 meters (20 ft)
- Diameter: 350 mm (35 cm)
- Wingspan: 1.35 m (4 ft 5 in)
- Range: 200 km (108 nmi)
- Speed: High subsonic, Mach 0.93 / 1,148 km/h (713 mph)
- Warhead: 165 kg (364 lb)
- Guidance system: Inertial guidance, Active radar homing and GPS guidance

The Exocet MM40 “Block 3c” variant: incorporates a digital Radio Frequency (RF) seeker into the missile, developed by Thales. This variant, known as Block 3c, is characterized as more resilient against jamming systems and can recognize surface vessels, leveraging advanced waveforms. The delivery of the Block 3c variant to the French Navy is set to commence in December 2022, with an additional order of 55 new missiles and 45 “MM40 Block 3c kits” to upgrade existing Block 3 missiles to the Block 3c configuration. In September 2023, tests conducted by the frigate Alsace confirmed the readiness of the variant for operational service.

In conclusion, the Exocet anti-ship missile stands as a testament to effective and adaptive missile technology. Born in the 1970s, its sleek design, sea-skimming capability, and autonomous targeting have made it a formidable force in naval warfare. From the early MM38 to the sophisticated MM40 Block III, continuous upgrades have ensured its relevance and effectiveness against evolving threats.
The Exocet anti-ship missile has a notable operational history, with its most prominent moment occurring during the Falklands War in 1982. Argentine Navy aircraft successfully deployed Exocet missiles against British naval forces, resulting in the sinking of the HMS Sheffield and the merchant vessel Atlantic Conveyor.
During the Gulf War in 1991, the Iraqi Navy employed Exocet missiles against coalition forces, damaging the USS Stark and other naval vessels. In subsequent conflicts, such as the 2006 Lebanon War and the ongoing conflicts in the Middle East, various Exocet variants have been used.
Apart from its use in conflicts, the Exocet has been widely adopted by naval forces worldwide and integrated into numerous platforms, contributing to its operational history. Continuous upgrades and advancements have sustained the missile’s relevance in modern naval warfare, making it a key player in maritime security.
As a symbol of precision and versatility, the Exocet remains a dynamic and ever-evolving component of modern naval arsenals, poised to meet the challenges of future maritime security with unwavering efficacy.

Important Announcement for Our Valued Readers!
After an article is published, it is possible that updates or changes may have occurred beyond the time of publication. Therefore, it is important to be aware that certain information in the article might be outdated. To ensure the most accurate analysis, it is highly recommended to verify the content with the latest sources available.
However, we are dedicated to delivering outstanding articles on military products and global updates. Maintaining quality and smooth operation requires resources. Your support sustains our efforts in providing insightful content. By purchasing high-quality products through our affiliated links, you help us keep our platform alive and acquire top-notch items. Your unwavering support is invaluable and inspires us to strive further.
We welcome your suggestions and requests for more information, as we value feedback from our readers. If there’s specific defence material or equipment not covered on our site, please share your request in the comments. We’ll strive to research and provide the required information. We sincerely thank you for your unwavering interest in our website, and we eagerly anticipate hearing from you! Enjoy your reading experience!

2 thoughts on “Explore the Best of the Exocet Anti-Ship Missile”